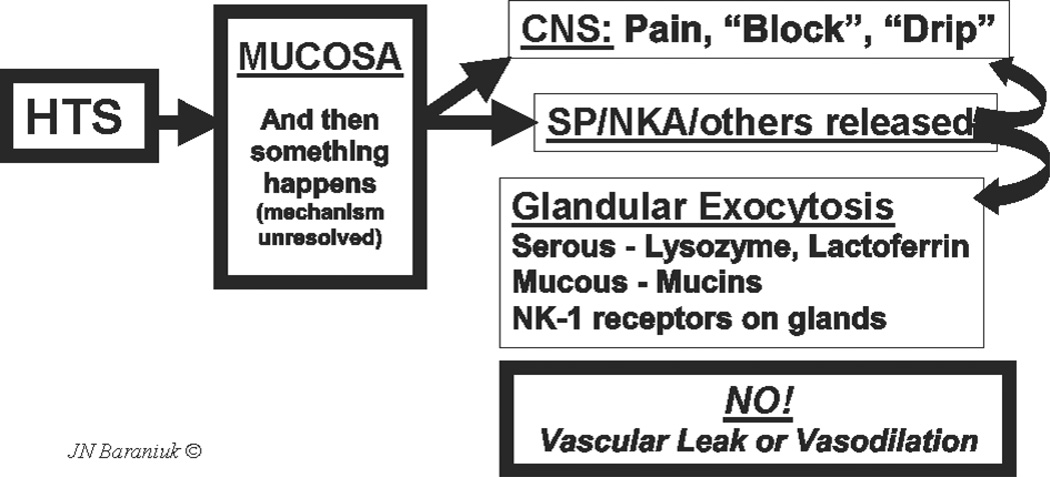
Fig. 1.
Axon response. Hypertonic saline (HTS) stimulates as yet unknown mechanisms in the nasal mucosa that lead to nociceptive nerve depolarization. This leads to central nervous system perceptions of pain, blockage or drip, and the local mucosal release of substance P (SP), neurokinin A (NKA) and potentially other neurotransmitters. Receptors for these tachykinins are localized to glands. This suggests that tachykinins released by the axon response mechanism near submucosal glands stimulate exocytosis of serous and mucous cell products. No changes in vascular permeability or vasodilation were detected indicating the absence of a vascular component to human airway axon responses.