Fig. 3.
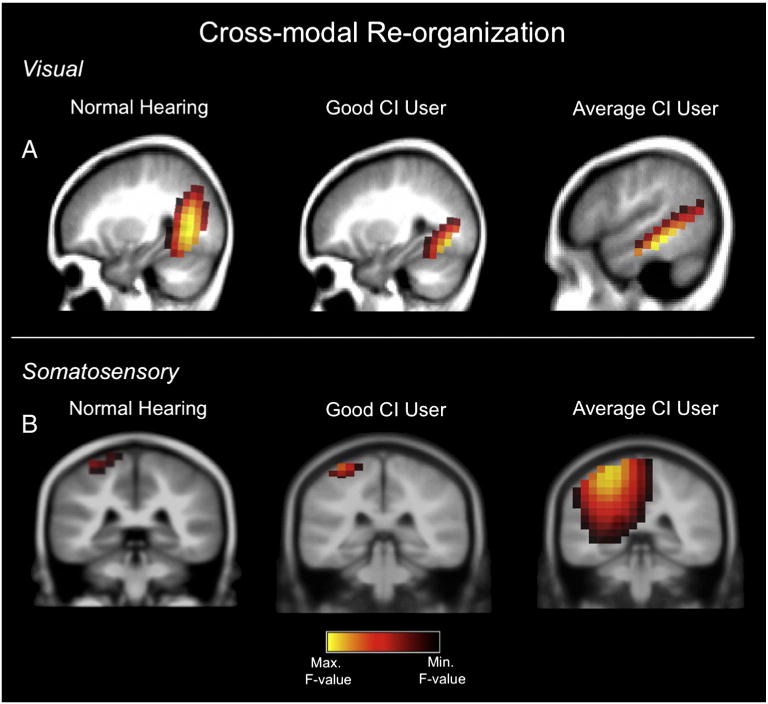
A. Visual cross-modal re-organization in children with cochlear implants. Visual gradient stimulation was presented to a child with normal hearing and two children with cochlear implants. Current density reconstructions (CDRs) of the cortical visual P2 component computed via sLORETA show activated regions as illustrated on sagittal MRI slices. Yellow regions reflect maximal cortical activation, while brown/black regions reflect the areas of least activation. Left panel: a 10 year-old child with normal hearing shows activation of higher-order occipital cortices in response to visual stimuli. Middle panel: an 8 year-old cochlear implanted child with a speech perception score of 96% on the Lexical Neighborhood Test, shows similar activation of higher-order visual areas, such as middle occipital gyrus, fusiform gyrus, and lingual gyrus. Right panel: in contrast, a 7 year-old cochlear implanted child with a speech perception score of 67% on the Multisyllabic Lexical Neighborhood Test shows activation of occipital areas and superior temporal gyrus and medial temporal gyrus. B. Somatosensory cross-modal re-organization in children with cochlear implants. Vibrotactile stimulation of the right index finger was presented to a child with normal hearing and two children with cochlear implants. Current density reconstructions (CDRs) of the cortical somatosensory N70 component computed via sLORETA show activated regions as illustrated in coronal MRI slices. Left panel: a normal hearing 7 year-old child shows activation of somatosensory cortex in the post-central gyrus. Middle panel: a 13 year-old cochlear implanted child with a speech perception score of 94% on the Consonant Nucleus Consonant (CNC) test shows similar activation of somatosensory cortex in post-central gyrus. Right panel: in contrast, a 15 year-old cochlear implanted child who showed average performance on the CNC speech perception test (76%) exhibited activation of the somatosensory cortex, superior and transverse temporal gyri, and parietal cortex.
