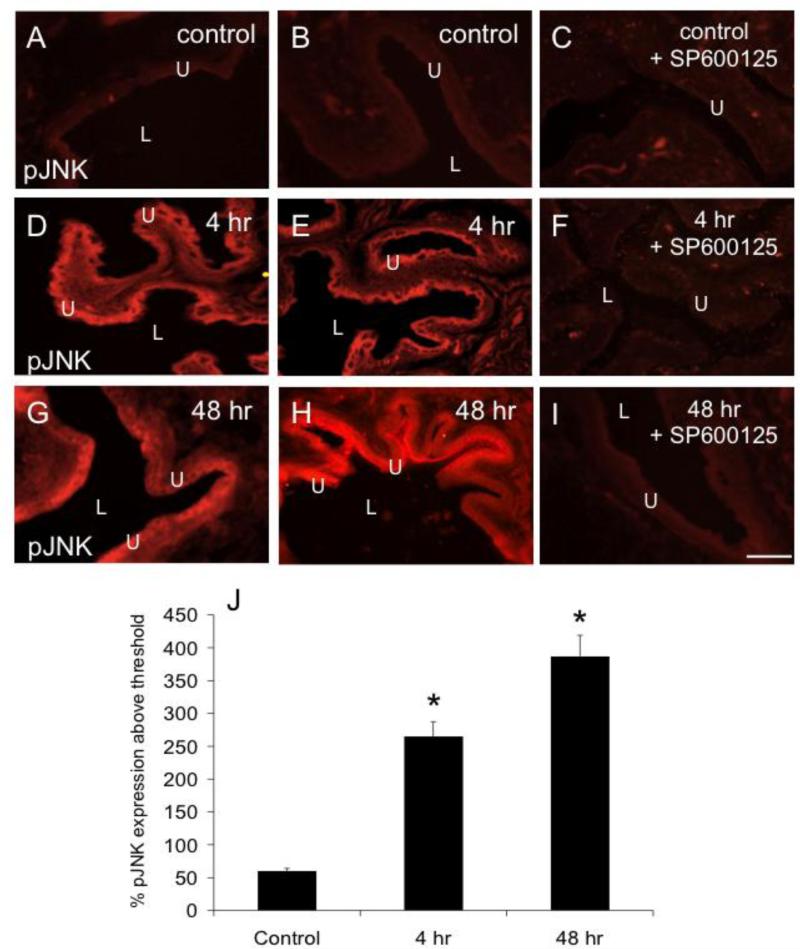
Figure 2.
CYP-induced cystitis increases pJNK expression in the urothelium (U). Fluorescence images of pJNK expression in urinary bladder sections of control (A, B), 4 hr (D, E), and 48 hr (G, H) CYP-treated rats. For all images, exposure times were held constant, and all tissues were processed simultaneously. In control rats, little if any pJNK expression was visible in the urothelium (U; A, B). CYP treatment (4 hr, D, E; 48 h, G, H) upregulated expression of pJNK in the urothelium in all layers (apical, intermediate and basal) of the urothelium. F, I: Intravesical instillation of SP600125 (25 μM) to block JNK phosphorylation reduced pJNK expression in the urothelium of rats treated with CYP (4 hr, F; 48 hr, I) but was without effect in control rats (C). J: summary histogram of pJNK expression in the urothelium with CYP treatment expressed a percentage of pJNK expression above threshold and averaged for all bladders from all conditions examined (n = 6). *P ≤ 0.01. L, lumen. Calibration bar represents 50 μm.