Figure 3.
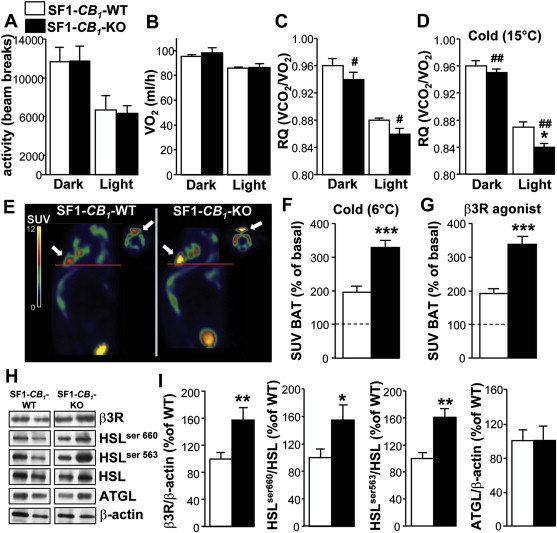
CB1 receptors in SF1-positive neurons regulate SNS activity, lipid oxidation and WAT lipolysis. (A) In-cage locomotor activity, (B) VO2 consumption and (C) respiratory quotient (RQ) during the dark and light phases determined in 15-weeks old chow-fed male SF1-CB1-WT and SF1-CB1-KO mice at 22 °C ambient temperature (n = 5–6). (d) RQ during the dark and light phases assessed in 15-weeks old chow-fed male SF1-CB1-WT and SF1-CB1-KO mice at 15 °C ambient temperature (n = 6). (E) Representative sagittal (main figure) and transverse (smaller insets) PET images showing 18F-FDG accumulation expressed as standard absorption values (SUV) in the BAT of chow-fed male SF1-CB1-WT and SF1-CB1-KO mice. Red lines indicate the image sections reported in the transverse views; images were from the study with the β3R agonist CL 316,243. SUV quantification after (F) 4 h exposure to 6 °C or (G) treatment with β3R agonist of chow-fed male SF1-CB1-WT and SF1-CB1-KO mice expressed as % of basal non-stimulated condition in the same animals (n = 6). (H) Representative western blot scans and (I) quantification of β3R, phospho-HSL ser 660, phospho-HSL ser 563, HSL and ATGL protein expression in the WAT of chow-fed male SF1-CB1-WT and SF1-CB1-KO mice maintained at 22 °C (n = 6–11; β-actin: loading control). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 genotype effect.
