Figure 3.
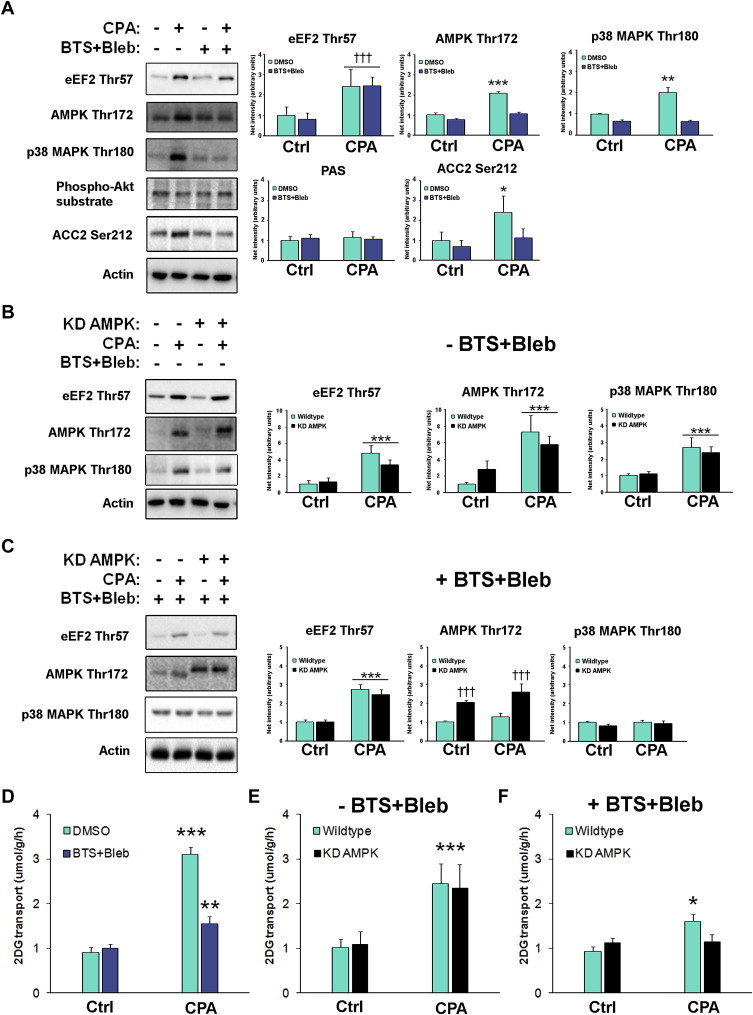
Cyclopiazonic acid (CPA)-induced glucose transport depends on AMPK and likely mechanical stress but not SR Ca2+. A) Quantifications of immunoblots from CPA-stimulated SOL muscles +/− BTS + Bleb. Quantified protein phosphorylation are indicated above the graphs throughout, n = 6, †††p < 0.001 ANOVA main-effect of CPA, */**/***p < 0.05/0.01/0.001 Tukey's post hoc test effect of CPA. B) Quantifications of immunoblots from CPA-stimulated wildtype and kinase-dead (KD) AMPK overexpressing SOL muscles, n = 6, ***p < 0.001 ANOVA main-effect of CPA. C) Quantifications of immunoblots from CPA-stimulated wildtype and KD AMPK overexpressing SOL muscles in the presence of BTS + Bleb. n = 6, p < 0.001 ANOVA main-effect of CPA, ††† ANOVA genotype main-effect. CPA-stimulated 2-deoxyglucose (2DG) transport (bottom graph) in mouse soleus D) +/− myosin ATP blockers E) in wildtype and KD AMPK mice F) combining myosin ATPase blockers with KD AMPK overexpression, n = 6. */**/***p < 0.05/0.01/0.001 CPA-effect using Tukey's post hoc test. Data are mean ± S.E.M.
