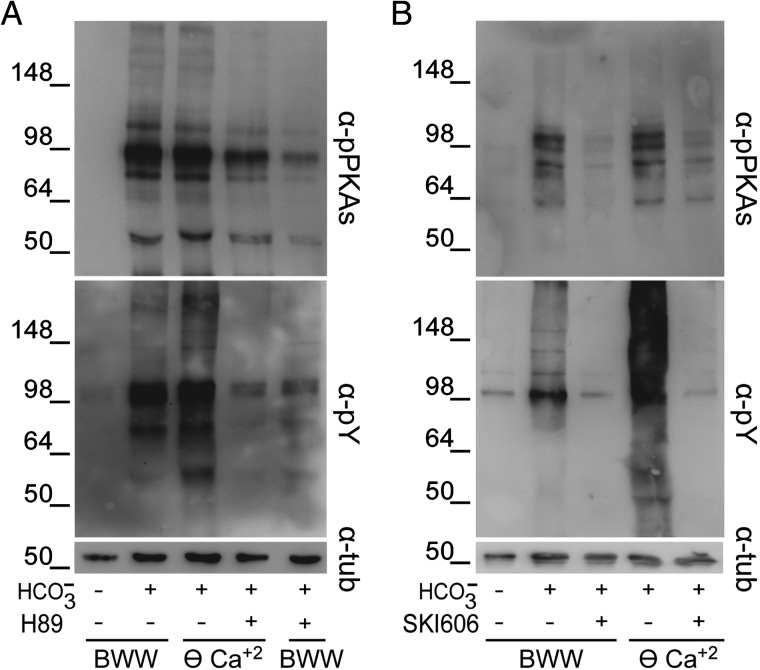
Figure 2.
Effect of the inhibition of cAMP/PKA or SFK/phosphatase signaling pathways on the [Ca2+]e-dependent increase in protein phosphorylation. Human sperm were incubated for 6 h in BWW or in ⊖ Ca2+containing either (A) the PKA inhibitor H89 (30 µM) or (B) the SFK inhibitor SKI606 (30 µM). In all cases, protein extracts were analyzed for both PKA substrate and Tyr phosphorylations by western blotting using α-pPKAs or α-pY antibodies, respectively (n = 3). β-Tubulin was used as the protein loading control.