Figure 1.
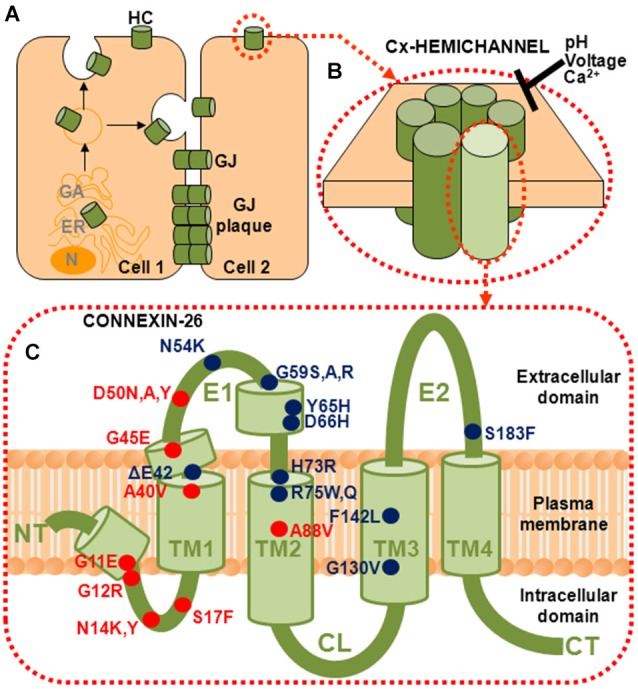
Connexins (Cxs) form gap junction (GJ) channels and hemichannels (HCs). (A) GJ channels are formed by of docking of two HCs from neighboring cells. GJ channels cluster into plaques and provide a direct intercellular communication pathway between cells. (B) HCs, also called connexons, can function in the plasma membrane in the absence of docking. They are hexamers of six Cx subunits and are strongly regulated by pH, voltage and divalent cations, principally Ca2+. (C) Topology of a Cx subunit. The amino (NT) and carboxy (CT) domains are oriented to the cytoplasm. The NT domain loops back into the membrane to contribute to the aqueous pore. There are four helical transmembrane domains (TM1–TM4) and two extracellular loop domains, E1 and E2. The short helical segments in NT and E1 identified in the crystal structure are also shown (Maeda et al., 2009). Locations of the 18 residues that have been associated with mutations causing syndromic deafness are indicated; those associated with KID syndrome are indicated in red.
