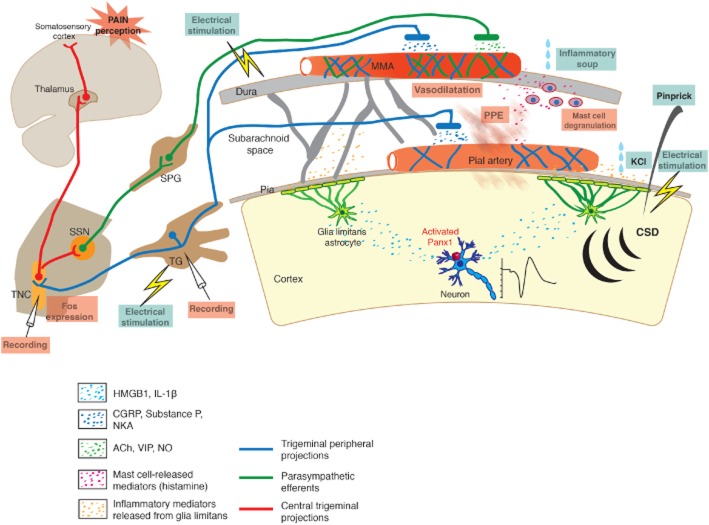
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the TVS mediating headache and some of the experimental methods used to activate it. Peripheral processes of the TG neurons terminate over the pial and dural vessels, whereas central processes terminate in TNC. Neurons in TNC project to thalamus and send collaterals to parasympathetic superior salivatory nucleus (SSN), which innervates dural vessels by way of spehenopalatine ganglion (SPG). Activation of TVS lead to release of several peptides and mediators from nerve endings around vessels, which induce dural vasodilatation, PPE and mast cell degranulation. TVS can be activated by electrical stimulation of the dura or TG, dural application of the inflammatory mediators (soup) as well as by CSD (evoked by pinprick, electrical stimulation or KCl). CSD stimulates trigeminal fibres around pial vessels by initiating a parenchymal inflammatory response triggered by the opening of neuronal pannexin-1 (Panx1) channels and release of HMGB1 and IL-1β. Activated nociceptors can be recorded from TG or TNC or detected by Fos immunolabelling in TNC. Dural vessel dilatation, PPE and mast cell degranulation can also be used to monitor TVS activation.