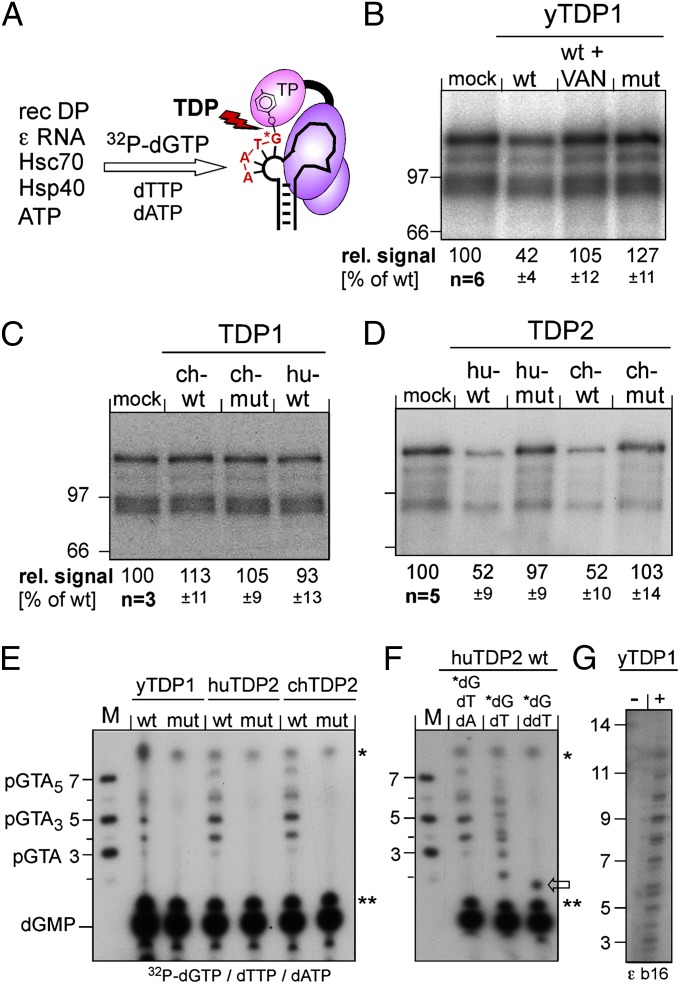
Fig. 4.
Both vertebrate TDP2s but only yTDP1 can cleave the P protein–DNA primer complex. (A) Assay principle. Recombinant DHBV P protein was activated in vitro to bind ε RNA, then incubated with [α32P]-dGTP plus dTTP plus dATP to initiate synthesis of the P-protein–linked primer. If P protein is a substrate for TDP, radiolabeling of P protein should be reduced by release of the labeled primer. (B–D) Impact on the radiolabeled P protein. Equal aliquots of the priming reaction were incubated with the indicated wild-type (wt) or mutant (mut) proteins or in buffer only (mock); in B, one reaction was performed in the presence of vanadate (VAN). Reactions were separated by SDS/PAGE, and labeled P protein (plus smaller degradation products) was visualized by autoradiography. The top bands were quantified by phosphorimaging. Mean values ± SD are indicated at the bottom of each panel. (E–G) Detection of released oligonucleotides. After incubation with the indicated TDP proteins, labeled nucleic acids were separated by electrophoresis in 20% polyacrylamide-7 M urea gels. M, 5′-32P–labeled marker DNA oligos of the indicated sequences and lengths. Bands marked with asterisks and double asterisks occurred in all reactions and are nonspecific. dGMP was identified by apyrase treatment of [α32P]-dGTP. In E, priming was performed with all three nucleotides required for the authentic primer. In F, [α32P]-dGTP was supplemented with only dTTP or ddTTP. In G, a variant ε RNA (ε b16) with a 16-nt bulge (5′ C in the bulge replaced by 5′ U2GU8) was used as priming template.