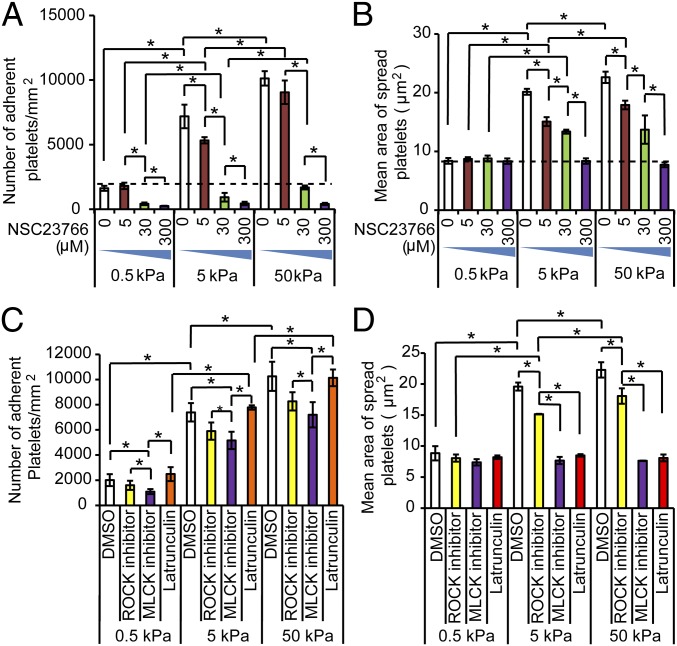
Fig. 2.
Rac1 mediates platelet mechanosensing during adhesion, whereas Rac1, myosin, and actin polymerization mediate platelet mechanosensing during spreading. (A) Rac1 inhibition attenuates platelet mechanosensing during adhesion on fibrinogen-conjugated PA gels in a dose-dependent fashion. (B) Likewise, Rac1 inhibition also attenuates platelet mechanosensing during spreading on fibrinogen-conjugated PA gels in a dose-dependent fashion. (C) The number of platelets treated with vehicle (DMSO) or other cytoskeletal inhibitors after adhering onto PA gels of different stiffnesses. Inhibition of ROCK, MLCK, or actin polymerization does not alter the substrate stiffness-mediated effects on platelet adhesion. (D) On the other hand, inhibition of ROCK, MLCK, or actin polymerization all attenuate the substrate stiffness-mediated effects on platelet adhesion. (*P < 0.05; n = 3 experiments; error bars indicate SD.)