Table 3. Optimization of the Asymmetric Varianta.
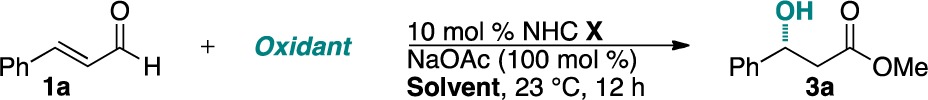
| entry | NHC | oxidant | solvent | yield (%)b | ee (%)c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
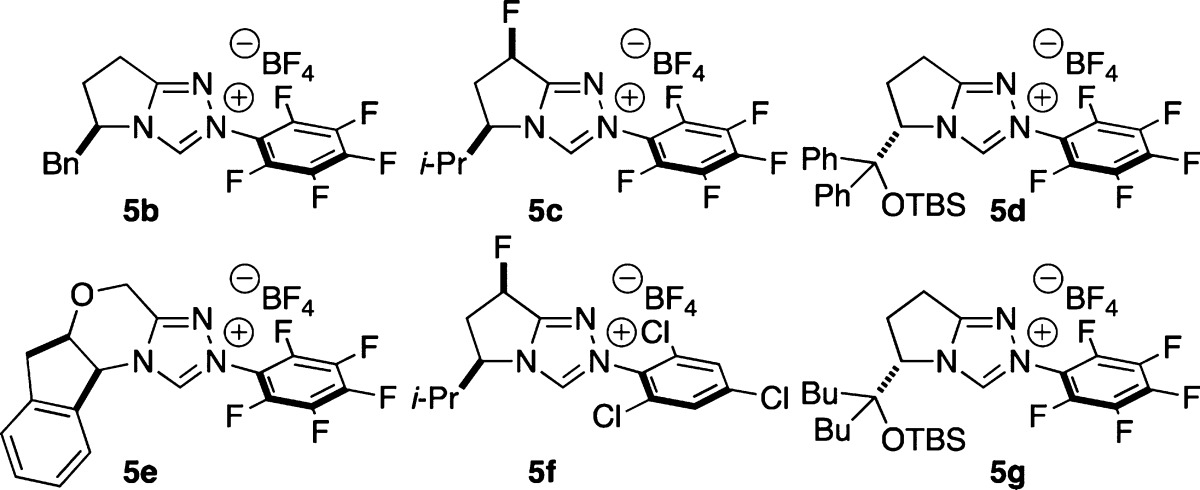
| 1 | 5b | 2a | MeOH | 39 | –25 |
| 2 | 5c | 2a | MeOH | 36 | –7 |
| 3 | 5d | 2a | MeOH | 15 | 66 |
| 4 | 5e | 2a | MeOH | 22 | 0 |
| 5 | 5f | 2a | MeOH | 42 | –8 |
| 6 | 5g | 2a | MeOH | 51 | 31 |
| 7 | 5g | 2a | DCM/MeOH (20:1) | 36 | 79 |
| 8 | 5g | 2a | toluene/MeOH (20:1) | 30 | 87 |
| 9 | 5g | 2a | trifluorotoluene/MeOH (20:1) | 44 | 88 |
| 10 | 5g | 2a | CCl4/MeOH(20:1) | 45 | 92 |
| 11 | 5g | 2d | CCl4/MeOH (20:1) | 34 | 84 |
| 12 | 5g | 2e | CCl4/MeOH (20:1) | 32 | 76 |
| 13 | 5g | 2f | CCl4/MeOH (20:1) | 12 | 16 |
Reactions were conducted with 1.0 equiv of 1a and 1.5 equiv of 2.
Isolated yields after chromatography.
Enantiomeric excess was determined by HPLC analysis on a chiral stationary phase.
