Figure 3. Categorization of lncRNA actions.
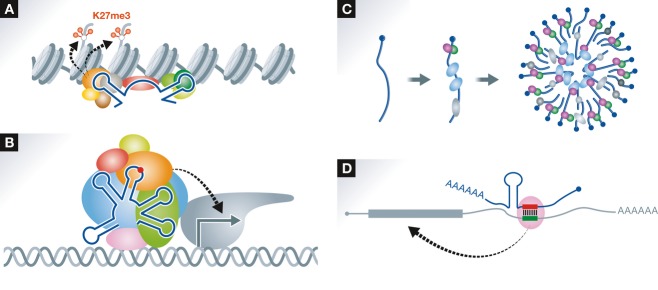
(A) lncRNAs recruit histone modification enzyme complexes such as PRC2 to specific chromosomal loci. The structural domain(s) within the lncRNA directly interacts with a subunit of the complex (e.g., EZH2). It remains to be elucidated how the lncRNAs recognize specific chromosomal loci. (B) lncRNAs act as transcriptional regulators. As an example, the lncRNA that acts as a transcriptional co-activator required for assembly of the transcription initiation complex is shown. An RNA modification shown by a red circle as well as distinct RNA structures are critical elements for the assembly. (C) lncRNAs act as structural cores of subcellular bodies (e.g., paraspeckles). The subcellular body is formed upon the assembly of multiple lncRNA–protein subcomplexes. (D) lncRNAs directly interact with specific mRNAs by base pairing. The base-paired duplex provides a binding platform for regulatory proteins (e.g., STAU1) that modulate mRNA stability and/or translation.
