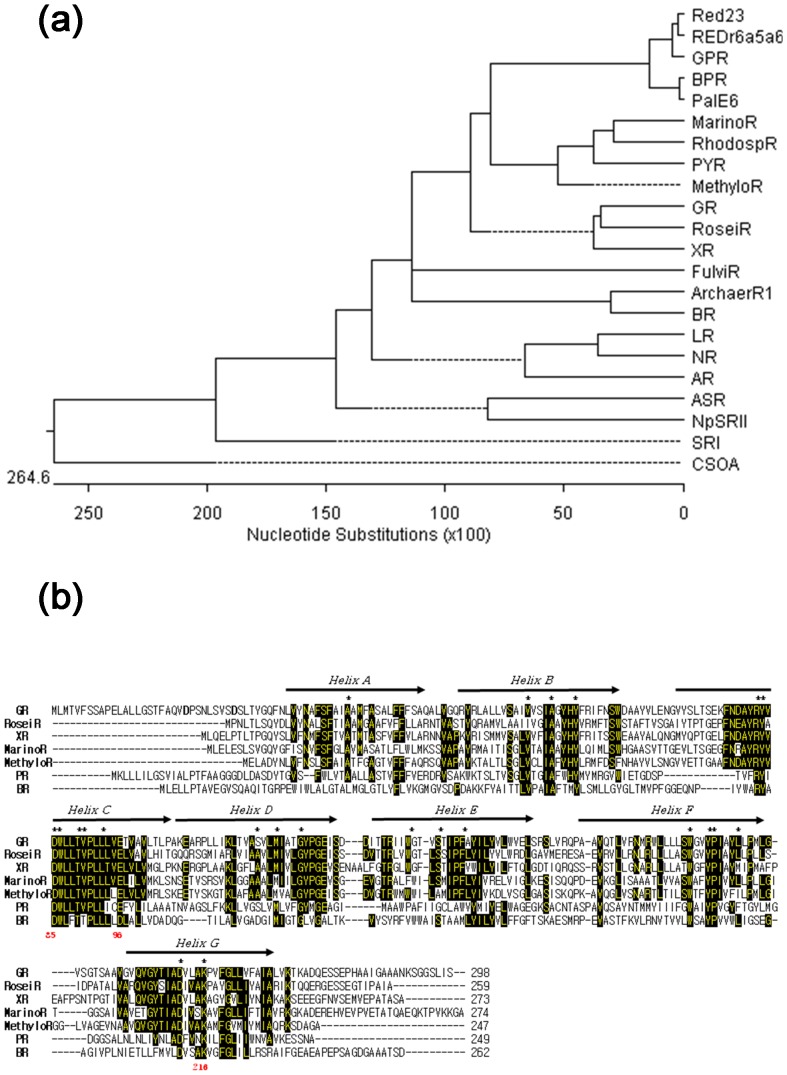
Figure 1. Pylogenetic tree and alignment.
(a) Phylogenetic tree of 22 microbial opsin sequences, representing phylogenetic relationship between Gloeobacter rhodopsin and related proteins from archaea to algae. Analysis was conducted by ClustalW. A dotted line on a phenogram indicates a negative branch length, a common result of averaging by the DNA STAR software. GR: Gloeobacter rhodopsin (accession number; NP_923144). Red23 and REDr6a5a2 were collected from Red Sea. GRP/BPR: green/blue-absorbing PRs. PalE6 was collected from Antarctic ocean. RhodospR: rhodopsin from Rhodospirillales sp. XR: Xanthorhodopsin from Salinibacter ruber. FulviR: rhodopsin from Fulvimarina. ArchaerR1: Archaerhodopsin 1. PYR: rhodopsin from Pyrocystis lunula. BR: Halobacterium salinarum bacteriorhodopsin. RoseiR: rhodopsin from Roseiflexus sp.MarinoR: rhodopsin from Marinobacter. MethyloR: rhodopsin from Methylophilales.LR: rhodopsin from Leptosphaeria maculans. NR: rhodopsin from Neurospora crassa. AR: rhodopsin from Acetabularia acetabulum. SRI: H. salinarum sensory rhodopsin I. NpSRII: Natronomonas pharaonis sensory rhodopsin II. ASR: sensory rhodopsin from Anabaena (Nostoc) sp.CSOA: Chlamydomonas reinhardtii sensory rhodopsin A. (b) Alignment of the sequences of GR, XR, PR, RoseiR, MarinoR, MethyloR and BR. GR contains the functionally important residues for proton transport, including homologues of Arg82, Asp85, Trp86, Asp96, Trp182, Tyr185, Asp212, and Lys216, with some of the numbering and helical segments (marked by arrows) for BR. There are 22 residues (marked with black boxes) common to all seven proteins (in one case, Asp/Glu substitutions). The Asp121 (Asp85 in BR) should be the proton acceptor of the retinal Schiff base. The Glu132 (Asp96 in BR) may be the proton donor.