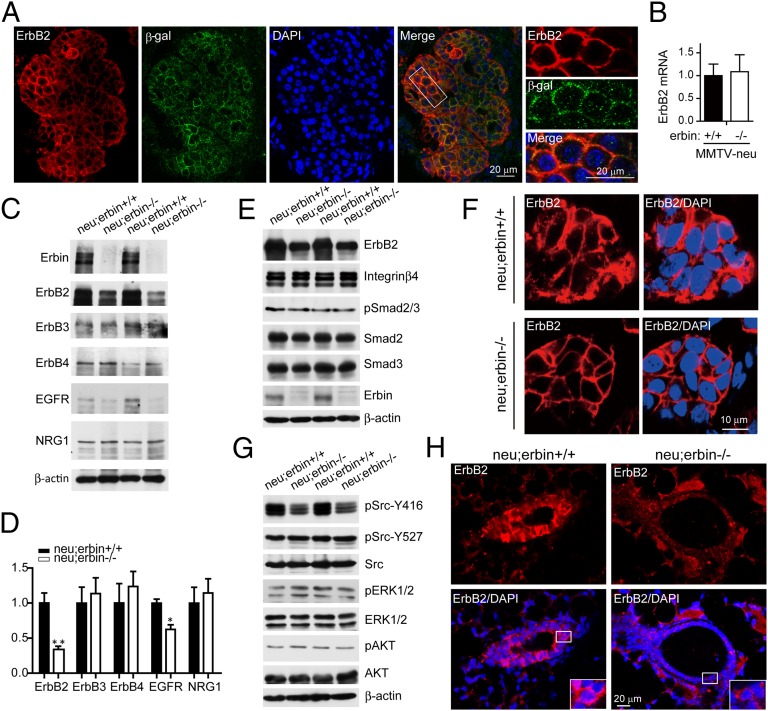
Fig. 4.
Depletion of Erbin reduced ErbB2 protein levels in breast tumor. (A) Colocalization of Erbin and ErbB2 in breast tumor cells. Tumor sections from neu;erbinΔC/ΔC mice were costained by rabbit anti-ErbB2 and chicken anti–β-gal antibodies. (B) Erbin depletion did not alter ErbB2 mRNA levels in breast tumors. Total RNA was subjected to quantitative RT-PCR. Results were normalized to internal control α-tubulin (n = 3; P > 0.05). (C) Decrease of ErbB2 proteins in tumor tissues of neu;erbin−/− mice. Breast tumors were isolated from indicated genotypes, homogenized, and blotted for indicated proteins. (D) Quantitative analysis of protein levels in C (n = 3; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). (E) Characterization of Erbin-interacting proteins in tumor tissues. Homogenates were blotted for indicated proteins. (F) Reduced ErbB2 immunoreactivity in individual breast tumor cells in neu;erbin−/− mice. Tumor sections were stained by rabbit anti-ErbB2 antibody. (G) Reduced Src activity in tumor tissues of neu;erbin−/− mice. Homogenates were blotted for indicated pan- or phosphorylated proteins. (H) Reduced ErbB2 immunoreactivity in epithelial cells of nontransformed mammary glands in neu;erbin−/− mice. Mammary sections were stained by rabbit anti-ErbB2 antibody.