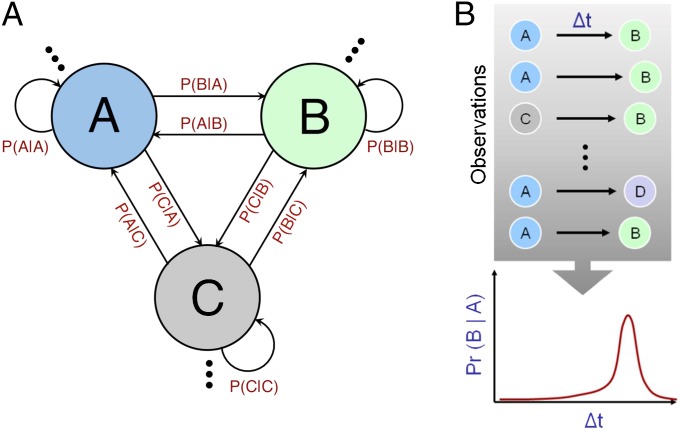
Fig. 1.
(A) A simple Markov system comprising probabilistically linked states. The domains that serve as diagnostic criteria for autism (language processing, social interactions, and behavioral repertoire) can all be modeled as temporally evolving Markov systems. The computation of transition probabilities is a key requirement for estimating a Markov system. (B) The task of transition probability estimation: from an observed temporal history of multiple state-to-state transitions, estimate P(B|A, Δt); the conditional probability of one state (“B”) given the other (“A”) and temporal duration, Δt, beyond A’s occurrence. The PIA hypothesis states that autism may be associated with inaccuracies in estimating this conditional probability and, hence, in one’s ability to discern predictive relationships between entities.