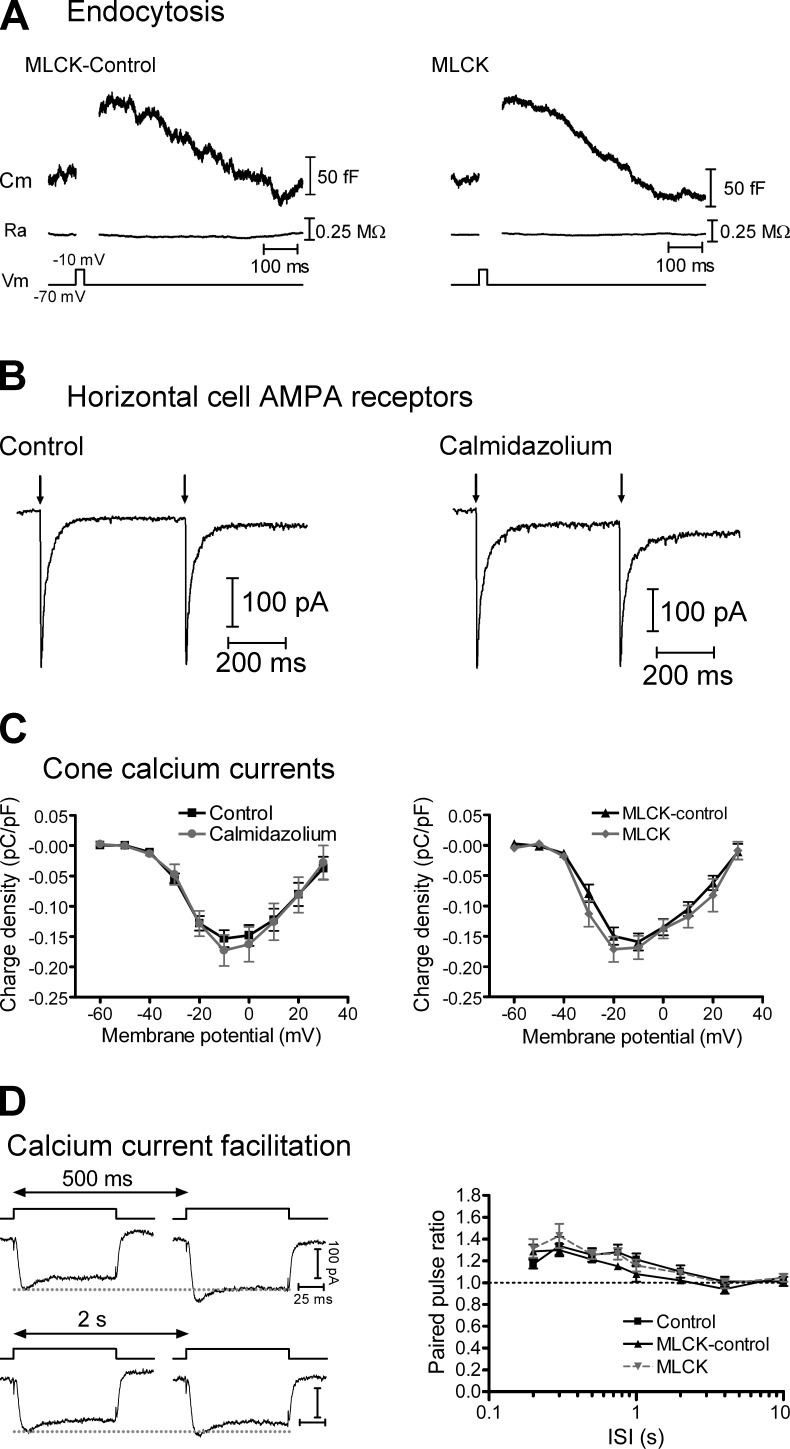
Figure 3.
CaM inhibitors do not affect rapid endocytosis, HC glutamate receptors, or cone Ca2+ currents (ICa). (A) Whole-cell capacitance recordings from cones that were dialyzed with either the MLCK-control (left) or MLCK (right) peptides (20 µM). There was a brief increase in whole-cell capacitance in response to a 25-ms depolarizing step to −10 mV from a holding potential of −70 mV, resulting from fusion of synaptic vesicles. The capacitance then decayed back toward baseline as vesicle membrane was retrieved via endocytosis. There was no change in access resistance (Ra). (B) Pairs of HC AMPA receptor currents were evoked by uncaging of MNI-glutamate (1 mM) with short (1 ms) UV flashes (500-ms interval) in control conditions (left) and, in a second HC, in the presence of 20 µM calmidazolium (right). Neither the amplitude nor the PPR was altered by calmidazolium. (C) Charge-voltage plots of leak-subtracted cone ICa recorded in response to 100-ms steps from −60 to 30 mV from a holding potential of −70 mV. The charge was normalized to whole-cell capacitance. Neither the amplitude nor the voltage dependence of ICa was affected by calmidazolium (20 µM, left) or the MLCK peptide (20 µM, right). (D) The PPR of Ca2+ charge (QCa2/QCa1) facilitated in response to pairs of depolarizing pulses (steps to −10 mV from −70 mV, 100-ms duration with intervals of 200 ms to 10 s). This facilitation was unaffected when cones were dialyzed with the MLCK or MLCK-control peptides. Mean ± SEM is shown.