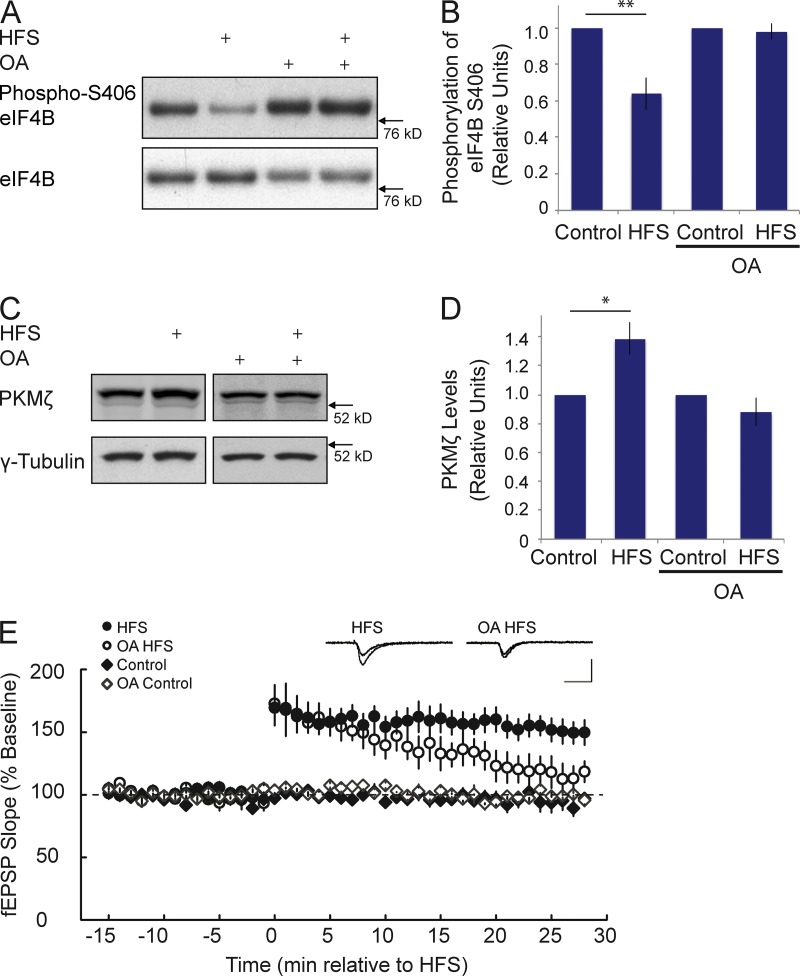
Figure 9.
PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation is required for PKMζ synthesis and is critical for the persistence of LTP in the CA1 field of hippocampus. (A and B) 2 min after delivery of HFS at the Schaffer collaterals, eIF4B S406 phosphorylation was significantly reduced. No such reduction was observed if HFS was delivered in the presence of OA. (B) Quantitative analysis. Signal intensities of phospho-S406 eIF4B were normalized against signal intensities of total eIF4B. Such signal intensities in HFS or OA HFS were again normalized to those in Control or OA Control. Student’s t test, P < 0.01 for HFS versus Control; P = 0.652 for OA HFS versus OA Control. n = 6. (C and D) 30 min after delivery of HFS at the Schaffer collaterals, levels of PKMζ were significantly increased. This increase was prevented in the presence of OA. (D) Quantitative analysis. PKMζ signal intensities were normalized against those of endogenous γ-tubulin. Such signal intensities in HFS or OA HFS were again normalized to those in Control or OA Control. Student’s t test, P < 0.05 for HFS versus Control; P = 0.266 for OA HFS versus OA Control. n = 4. (E) LTP was induced at CA3-CA1 synapses by HFS. Expression of LTP was blocked by OA. Sham stimulation (Control) was performed as described in the Materials and methods. Inset traces show superimposed representative fEPSPs recorded during the baseline period (top trace) and at 30 min after HFS (bottom trace), in a vehicle-treated control slice (left) and a slice treated with OA (right). Calibration: 1 mV, 20 ms. n = 7 for HFS, n = 4 for OA HFS, n = 6 for Control, n = 4 for OA Control. Quantitative analysis (one-way ANOVA): F3,17 = 11.20, P < 0.001. Tukey post-hoc analysis: HFS versus Control, P < 0.05; HFS versus OA Control, P < 0.05; HFS versus OA HFS, P < 0.05. Error bars represent SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.