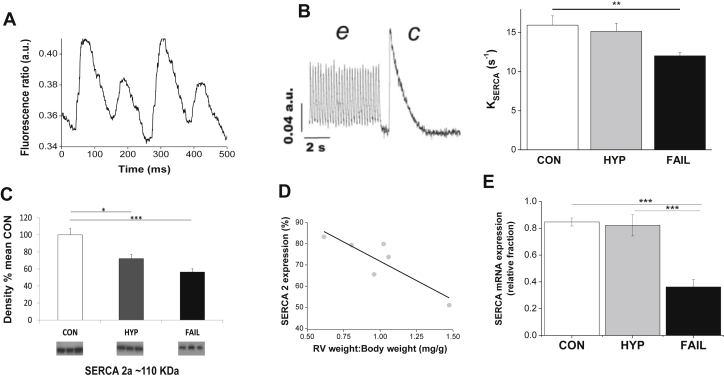
Fig. 3.
A Intracellular Ca2+-transient (Fura-4F fluorescence) alternans for a RV myocyte isolated from a FAIL animal stimulated at 9 Hz. B SERCA activity estimated as KSERCA was significantly reduced in RV myocytes from FAIL animals. KSERCA was calculated as the difference between the rate constant of decay of the electrically stimulated Ca2+-transient at 5 Hz (e, representing Ca2+ removal by SERCA and Na–Ca exchange) and caffeine stimulated Ca2+ transient (c, representing Ca2+ removal by Na–Ca exchange). C Levels of SERCA protein, estimated by Western blot, were significantly lower in HYP and FAIL RV myocardium than CON (data expressed as % of the mean density of CON samples, N = 6 in each group) D. In the HYP group SERCA density was significantly correlated with the RV weight:body weight ratio R2 = 0.7, P < 0.05). E Levels of mRNA for SERCA, estimated by real-time RT-PCR, were significantly lower in FAIL myocardium than HYP or CON (data expressed relative to a calibrator sample normalised to the housekeeper gene 18S, N = CON 12, HYP 7, FAIL 14). A and B modified from (Benoist et al., 2012). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.