Figure 1.
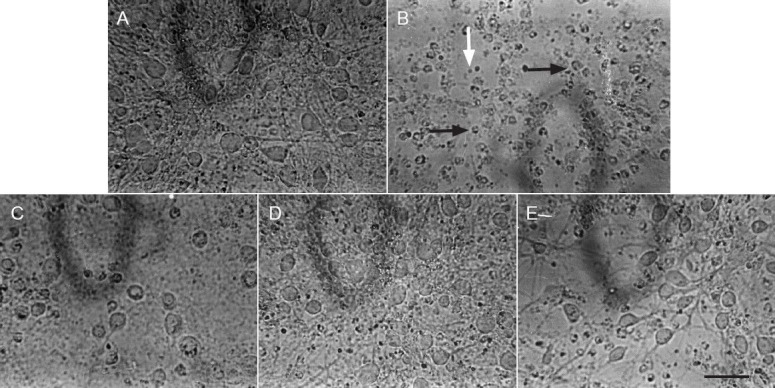
Serum containing flavonoids from the stems and leaves of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi lessens potassium cyanide-induced injury in primary cultured neurons in rats (× 400).
(A) Primary cortical neurons from the control group. (B) Primary cortical neurons from the potassium cyanide-treated group. Primary cortical neuron exposed to 1 mmol/L potassium cyanide for 60 minutes showed that the count and volume of cells were notably decreased, cell neuritis and reticular structure disappeared and the cells assumed a rounded shape with a rough cell membrane (black arrows), and there were many dead and fragmented cells (white arrow). (C–E) Primary cortical neurons from the groups exposed to flavonoids from the stems and leaves of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi groups at doses of 18.98, 37.36, 75.92 μg/mL for 24 hours, followed by exposure to potassium cyanide (1 mmol/L) for 60 minutes, respectively. Cell morphology was observed and photographed by reversed microscopy.
