Table 1.
Optimized Catalyst for Allyl-Allyl Couplings
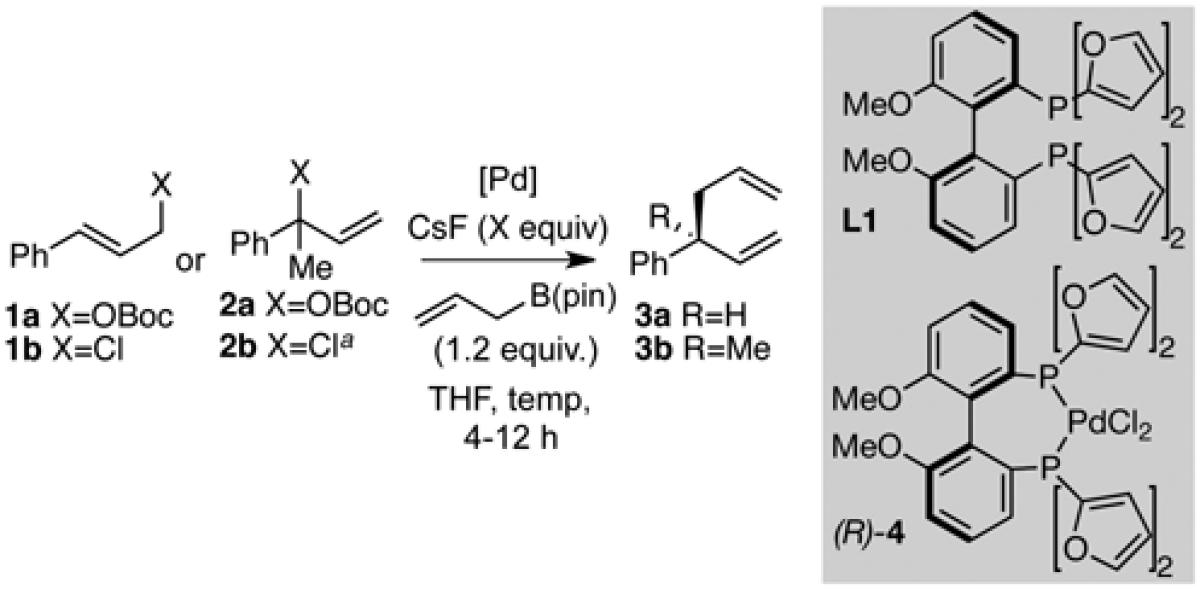
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | catalyst | substrate | CsF (equiv) |
t (h) | T (°C) | yield (%)b |
erc |
| 1 | 5% Pd2(dba)3
10% L1 |
1a | 0 | 12 | 60 | 72 | 96:4 |
| 2 | 0.25% (R)−4 | 1a | 0 | 8 | 60 | 0 | - |
| 3 | 0.1% (R)−4 | 1a | 0.05 | 4 | 60 | 95 | 96:4 |
| 4d | 0.1% (R)−4 | 1a | 0.05 | 4 | 60 | 96 | 96:4 |
| 5 | 0.1% (R)−4 | 1b | 3 | 5 | rt | 92 | 97:3 |
| 6e | 2% Pd2(dba)3
4% L1 |
2a | 3 | 12 | 60 | 86 | 96:4 |
| 7e | 0.25% (R)−4 | 2a | 3 | 4 | 60 | 59 | 94:6 |
| 8e | 0.25% (R)−4 | 2b | 5 | 5 | rt | 85 | 98:2 |
a The linear isomer of chloride was used.
Yield of purified material, average of two or more experiments.
Enantiomer ratios were determined by GC analysis on a chiral stationary phase and are an average of two or more experiments.
Reaction set up on benchtop and purged with N2.
Reaction run in 10:1 THF/H2O.
