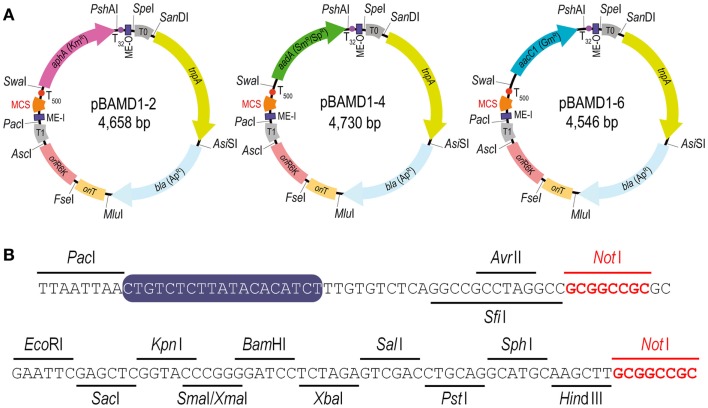
Figure 1.
Functional features of the pBAMD1-x delivery vectors. (A) Schematic representation of the pBAMD1-x plasmid series. The functional elements of each plasmid include the relevant restriction sites used for assembling the vectors, the antibiotic-resistance markers (Ap, ampicillin; Km, kanamycin; Sm, streptomycin; Sp, spectinomycin; and Gm, gentamicin), the hyper-active TnpA transposase encoded by tnpA, a conditional origin of replication [ori(R6K)] dependent of the π protein, an origin of transfer (oriT), two mosaic elements (termed ME-I and ME-O), the transcriptional terminators T0 and T1 located just outside the transposon module, and a multiple cloning site (MCS) compatible with any plasmid belonging to the Standard European Vector Architecture (SEVA) initiative (Silva-Rocha et al., 2013; Durante-Rodríguez et al., 2014). Note that the antibiotic-resistance gene determines the full name of each plasmid. (B) Restriction enzymes targets within the multiple cloning site of the pBAMD1-x delivery vectors (x = 2, KmR; x = 4, SmR/SpR; and x = 6, GmR). The MCS starts with the unique AvrII/SfiI recognition sites, and two NotI recognition sites (highlighted in red) were included in the MCS sequence to enable the consecutive assembly of different cargos from the SEVA collection. The sequence of ME-I is indicated by a purple box.