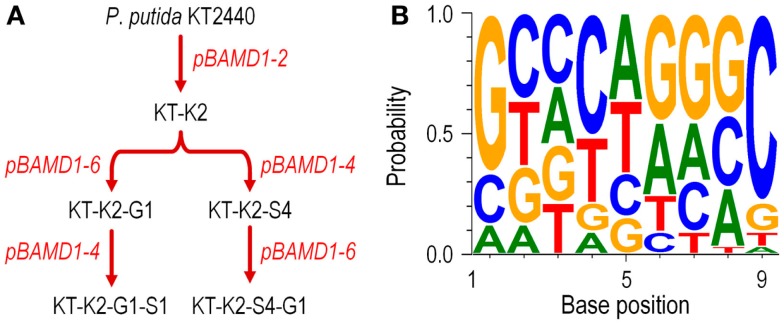
Figure 2.
Functional characterization of the pBAMD1-x delivery vectors in P. putida KT2440. (A) Sequential insertion of different mini-Tn5 modules from pBAMD1-x plasmids carrying all the three possible antibiotic-resistance determinants. The flowchart shows the procedure followed for the combinatorial integrations, starting from the wild-type strain KT2440. The names given to the intermediate strains reflect the order in which each antibiotic was delivered into the recipient bacteria (K, kanamycin; S, streptomycin/spectinomycin; and G, gentamicin). The exact chromosomal localization of the insertions in these strains is given in Table 3. Plasmids used in each round of integration are indicated in red. (B) Assessment of the possible sequence preference in the target DNA during the insertion process of the pBAMD1-x delivery vectors in P. putida KT2440. The WebLogo 3.4 software was used to identify the DNA signature (if any) in which the transposon lands in the chromosome of recipient bacteria. The software was fed with the 9-bp DNA sequence targeted by mini-Tn5 in independent trials (Table 3). Note the slight preference for G/C pairs at both ends of the target DNA motif (i.e., in positions 1 and 9).