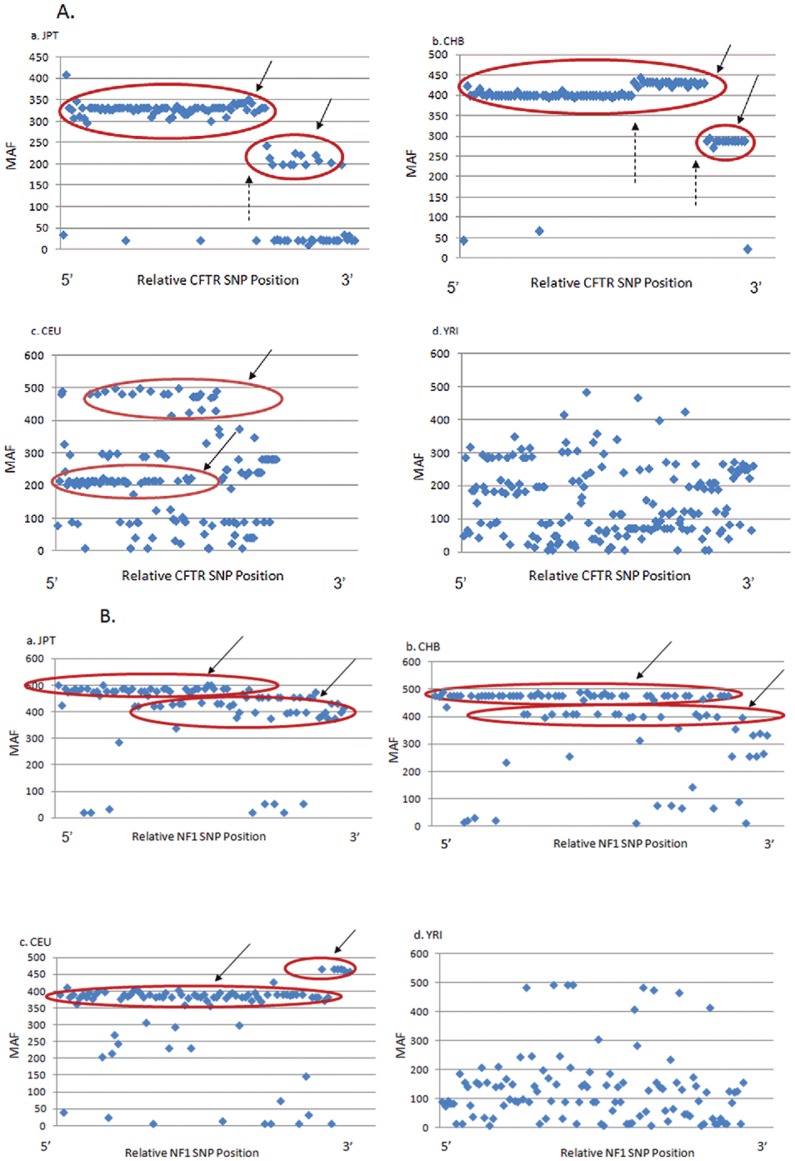
Figure 3. HapMap minor allelic frequencies (MAFs) plotted against gene sequence position.
Frequency data for SNPs in CFTR (Panel A) or NF1 (Panel B) were collated for each of the ethnicities shown: JPT (Japanese in Tokyo, 45 individuals); CHB (Han Chinese in Beijing, 45 individuals); CEU (or CEPH, Utah residents with ancestry from northern and eastern Europe, 90 individuals); and YRI (Yoruba in Ibidan, Nigeria, 90 individuals). MAF refers to the relative frequency (1000 = 100% incidence) of the minor allele at each SNP position. Solid arrows/red circles depict areas indicative of a haplotype block (also referred to as MAF block) in the genes as shown; broken arrows describe sites of genomic recombination. In order to generate a MAF block diagram, allele frequency data was downloaded from UCSC genome table browser (http://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hg:tables). After downloading, SNPs with MAF equal to zero among all four ethnicities were omitted. The remaining SNPs were then inserted into the scatter plot. Linkage disequilibrium valves for the blocks depicted here (when obtained directly from HapMap) were robust (r2 among co∶allelic SNPs shown by red circles typically = 1.0).