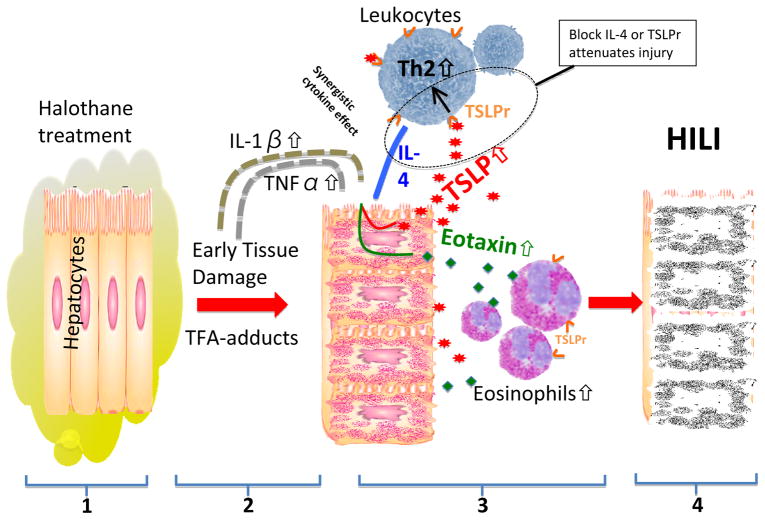
Figure 1.
(1) Mice treated with halothane produce disruptive trifluoroacetylated (TFA) protein adducts in hepatocytes. (2) This early damage causes an increase in IL-1β and TNFα levels. (3) Along with IL-4, these cytokines synergistically cause an upregulation of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and eotaxin in hepatocytes. Secreted TSLP binds to its receptor (TSLPr) on lymphocytes causing a Th2 response that among other things increases IL-4 secretion. Hepatocyte eotaxin levels are also increased by the elevated trio of cytokines which in turn participates in the recruitment of tissue damaging eosinophils that produce (4) the halothane induced liver injury (HILI). Interfering with IL-4 or TSLPr attenuates the injury in this model.