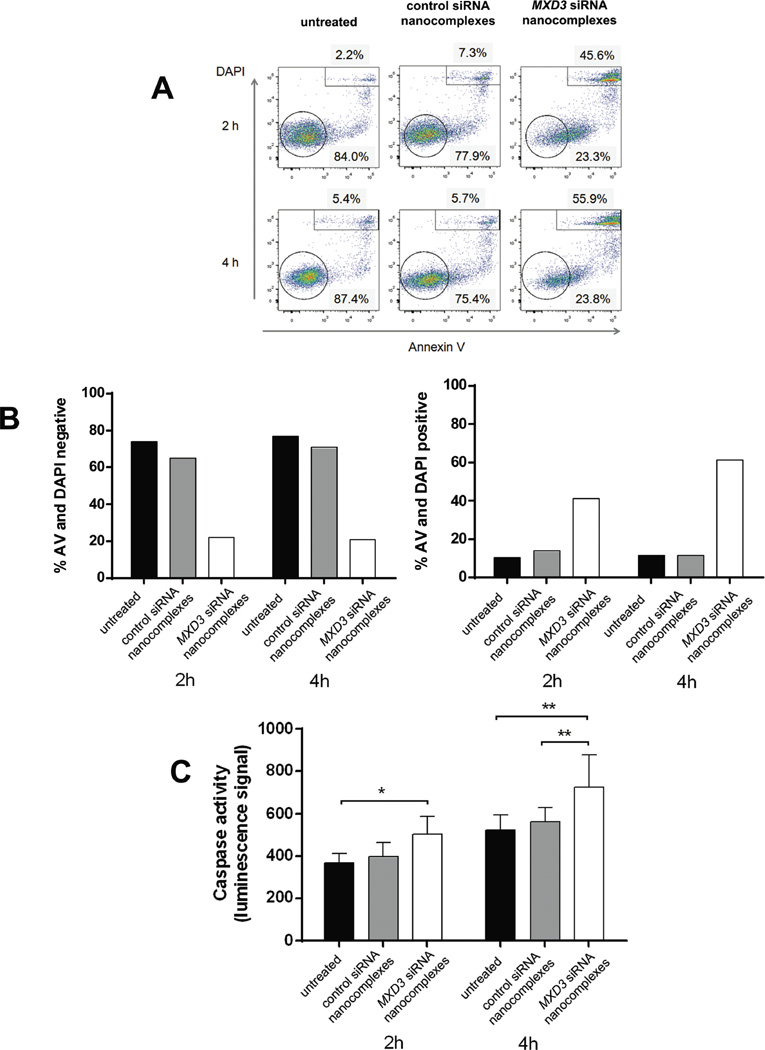
Figure 4. Treatment of Reh cells with the MXD3 siRNA-αCD22 Ab-SPIO NPs increases apoptosis.
(A and B) Cell death measured by annexin V and DAPI. (A) Reh cells treated with the MXD3 siRNA-αCD22 Ab-SPIO NPs had fewer live cells (negative for annexin V and DAPI) and more dead cells (positive for annexin V and DAPI) than untreated cells or cells treated with the control siRNA-αCD22 Ab-SPIO NPs at 2 and 4 h after treatment. The circled or rectangle events indicate double negative or double positive cells, respectively. Graphs show one representative experiment (from a total of 2 experiments repeated).
(B) Flow cytometry results at 2 and 4 h from 2 experiments. Data as mean (n = 2 for each time point). The MXD3 siRNA nanocomplex-treated cells showed significantly fewer double negative cells and significantly more double positive cells at both time points: double negative (vs. untreated p = 0.0000154, vs. control p = 0.0000484) and double positive (vs. untreated p = 0.0006531, vs. control p = 0.0008478). This analysis used a three-way ANOVA with Treatment, Time and Experiment Number as factors. The p-values are from the post-hoc Tukey studentized range test.
(C) Cell death measured by caspase 3 and 7 activities. Cells were treated the same way as in (A) with the same control. Histograms represent caspase activity measured by luminescence signal at 2 and 4 hours after treatment. Data include 2 independent experiments. Data as mean ± SD. (n = 9 for each time point). We used a two-way ANOVA on Treatment and Time, with post-hoc comparisons from the Tukey studentized range test. The cells treated with the MXD3 siRNA nanocomplexes had a significantly higher average caspase 3 and 7 activity levels than either the untreated cells (p = 0.0127) or those treated with the control siRNA nanocomplexes (p = 0.0380)
αCD22 Ab, anti-CD22 antibody; SPIO, superparamagnetic iron oxide; NP, nanoparticle; siRNA, small interfering RNA; AV, Annexin V; DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.