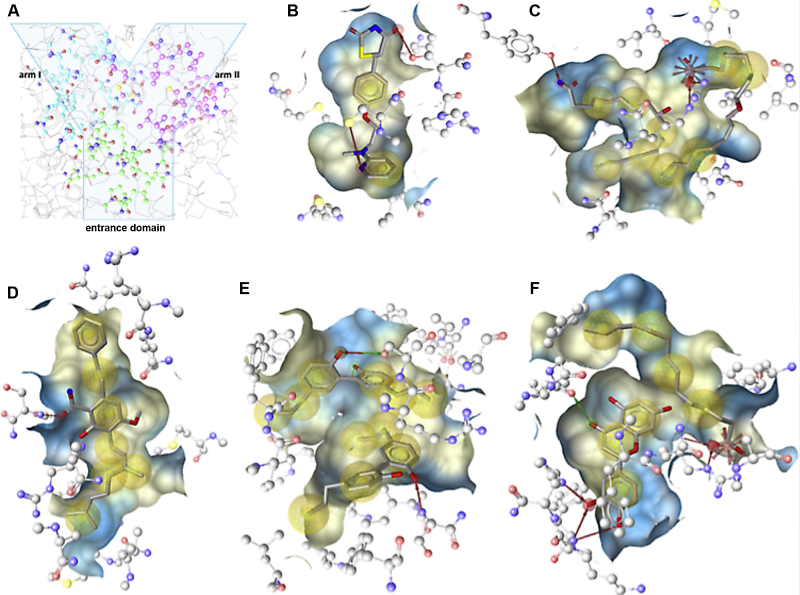
Fig. 2.
Binding modes of selected PPARγ ligands co-crystallized with PPARγ. (A) The Y-shaped PPARγ LBD composed of one entrance domain and two arms (arm I is substantially polar, arm II is mainly hydrophobic) [174]. Observed protein-ligand interactions are presented between the human PPARγ LBD and (B) the synthetic agonist rosiglitazone (PDB: 4ema), (C) the endogenous agonist 9-(S)-HODE binding as a homodimer (PDB: 2vsr), the natural ligands (D) amorfrutin B (PDB: 4a4w), (E) magnolol binding as homodimer (PDB: 3r5n), and (F) luteolin binding as a mixed dimer with myristic acid (PDB: 3sz1). The interactions were visualized by means of the software LigandScout [254] with the following color code: hydrogen bond acceptor (red arrow), hydrogen bond donor (green arrow), hydrophobic interaction (yellow sphere), and negative ionizable area (red star). The ligand binding pocket is depicted as surface; its colors are based on the lipo- and hydrophilicity. Contacts with active site water molecules are not shown.