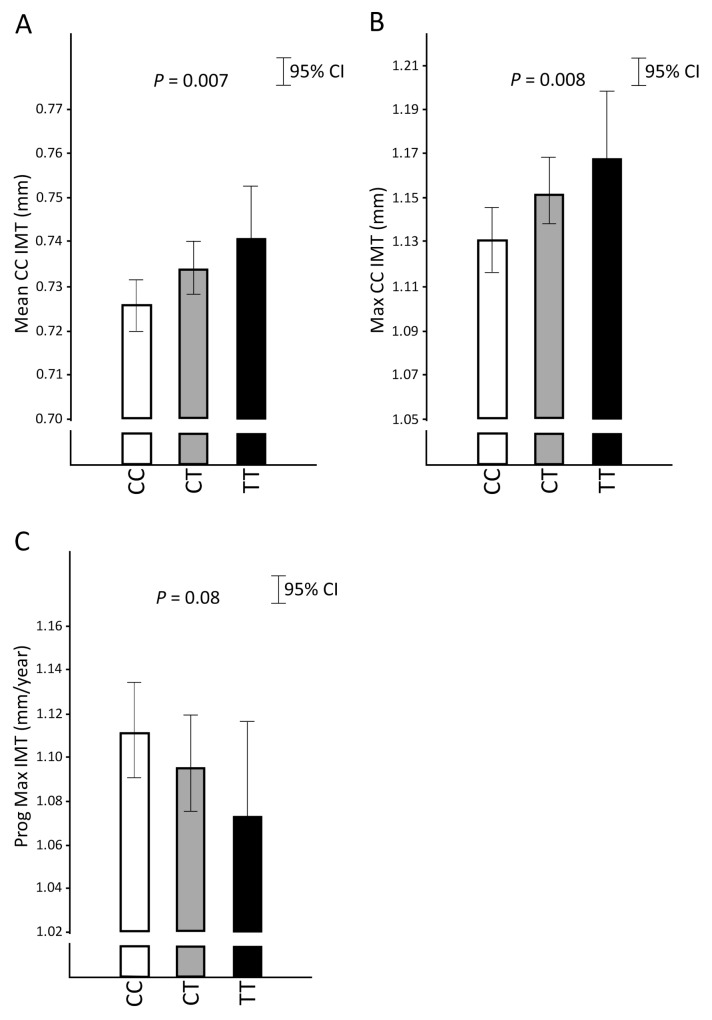
Figure 2.
The minor T allele of rs2453021 in CD137 was associated with increased intima-media thickness (IMT) in the common carotid (CC) artery independently of vascular risk factors. IMT was measured by high-resolution ultrasonography in the IMPROVE cohort. Participants had at least three risk factors of CVD at the time of enrollment but were free of clinical disease. Measurements were made at baseline and at 15 and 30 months. Thirty-month progression of IMT (Prog CC-IMT) (change over time; in mm/year) was calculated by linear regression considering all three time points (0, 15 and 30 months). Values are mean CC-IMT (Mean CC-IMT; in mm) (A), maximum CC-IMT (Max CC-IMT; in mm) (B) and maximum IMT progression (Prog Max IMT; in mm/year) (C) according to rs2453021 genotype. Results are adjusted for sex, age, cardiovascular risk factors (hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypoalphalipoproteinemia, hypertension, diabetes, current smoking, smoking pack-year categories, body mass index [BMI] and CRP) and genetic background (MDS) (model 3). The antilog of mean levels with 95% CI of logarithmically transformed data are shown. Linear regression P values are indicated. Genotype: CC, homozygote major C allele; CT, heterozygote; TT, homozygote minor T allele.