Figure 5.
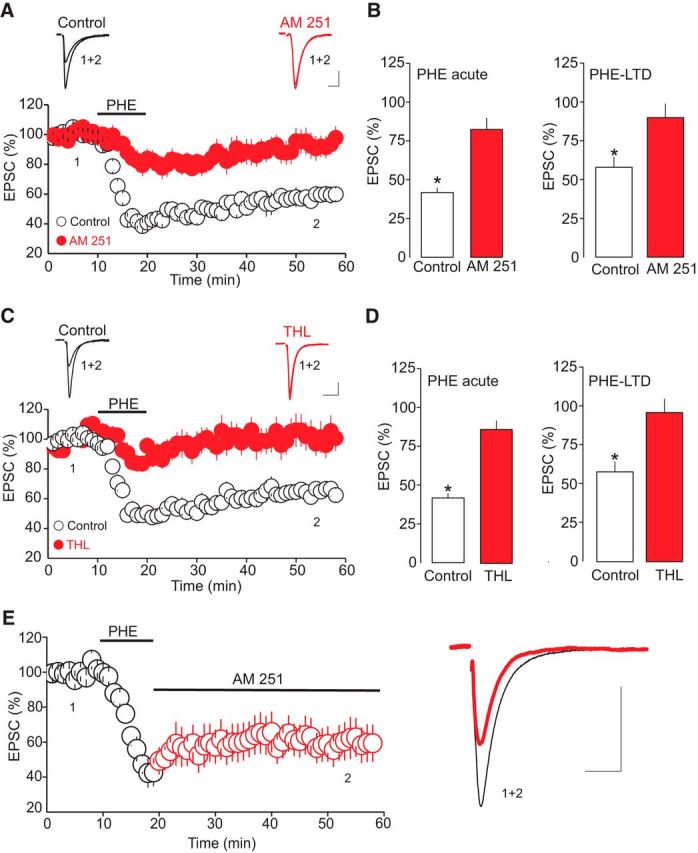
The presynaptic expression of the α1-AR LTD is mediated by 2-AG. A, Blockade of the CB1 receptor with AM 251 markedly reduces both the acute inhibition of AMPAR-EPSCs and the magnitude of the α1-AR LTD. Bottom, Summary graph of the effect of PHE (100 μm) on the amplitude of AMPAR-EPSCs obtained in the control condition (white circles, n = 12) and in the presence of AM 251 (3 μm, filled red circles, n = 8). Top, Superimposed AMPAR-EPSC traces (30 trials) collected before (1), during α1-AR LTD (2), and recorded in the absence (white circles) and presence of AM 251 (filled red circles). B, Summary graphs of the α1-AR-induced acute depression of AMPAR-EPSCs (left) and LTD (right) obtained in the control condition (open bars) and in the presence of AM 251 (filled bars). *p < 0.05. C, Blockade of 2-AG synthesis inhibits both the acute depression of AMPAR-EPSCs and LTD induction by α1-ARs. Bottom, Summary of the effect of PHE (100 μm) on the amplitude of AMPAR-EPSCs obtained in the control condition (white circles, n = 12) and in slices treated with THL (10 μm, filled red circles, n = 8). Top, AMPAR-EPSC traces recorded before (1) and during (2) α1-AR LTD. D, Summary histograms of the α1-AR-induced acute depression of AMPAR-EPSCs (left) and LTD (right) obtained in the control condition (open bars) and in the presence of THL (filled bars). E, The α1-AR LTD is not mediated by a sustained activation of CB1 receptors. Left, The effect of AM 251 (3 μm) applied after PΗΕ administration on the magnitude and time course of the α1-AR LTD. Blockade of CB1 receptors after the initiation of α1-AR LTD did not reverse the LTD (n = 8). Right, Superimposed AMPAR-EPSC traces at time points indicated by number in left graph. Calibration: 50 pA, 10 ms.
