Figure 7.
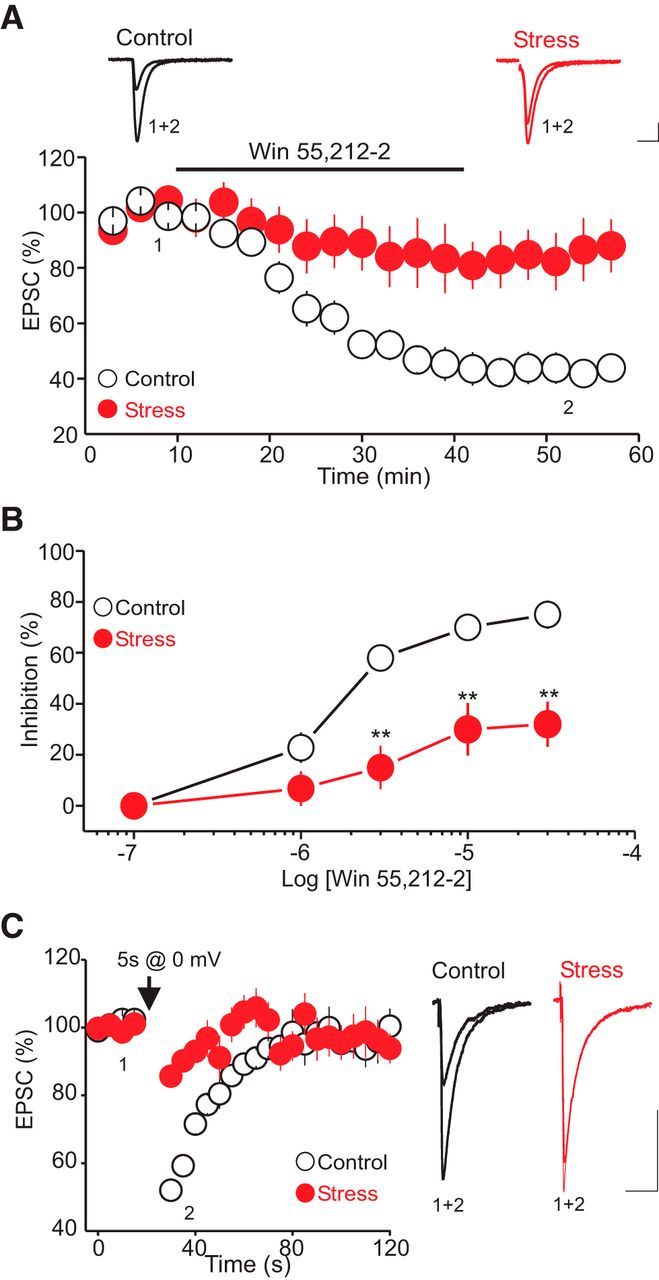
Exposure to CRS impairs the function of presynaptic CB1 receptors in the DRn. A, CRS reduces the ability of presynaptic CB1 receptors to inhibit glutamate release. Top, Superimposed AMPA-EPSCs taken before and during bath application of the CB1 receptor agonist WIN 55212-2 (10 μm) in control (left) and CRS-exposed rats (right). Calibration: 50 pA, 10 ms. Bottom, Summary graph of the inhibition of AMPA-EPSC amplitude induced by WIN 55212-2 (10 μm) in control (white circles, n = 13) and CRS-exposed rats (red circles, n = 10). CRS exposure profoundly reduces the efficacy of WIN 55212-2 in inhibiting the amplitude of AMPAR-EPSCs. B, Dose–response curves of the effect of WIN 55212-2 on AMPAR-EPSCs obtained in control (white circles) and CRS-exposed rats (red circles). **p < 0.01. C, Exposure to CRS profoundly reduces the magnitude of the eCB-mediated DSE. Left, DSE induced in control (white circles, n = 14) and CRS-exposed rats (red circles, n = 12). Right, Superimposed AMPAR-EPSCs traces taken before and during the DSE in putative DRn 5-HT neurons from control and CRS-exposed rats. Calibration: 50 pA, 10 ms.
