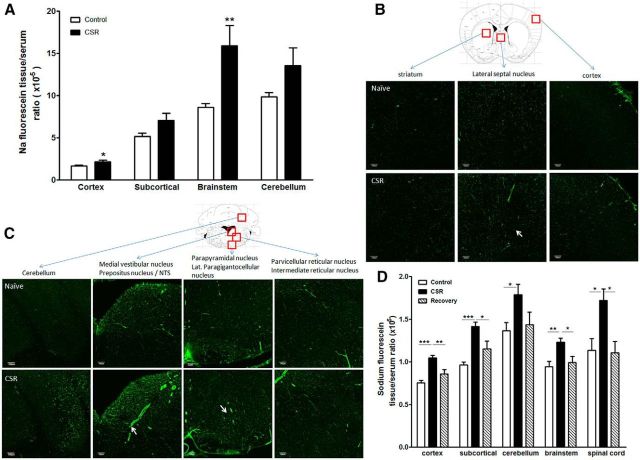
Figure 7.
Effect of CSR on BBB permeability. A, Sodium fluorescein uptake 10 min after intravenous injection in anesthetized mice was increased in cerebral cortex and brainstem in the CSR group (n = 5) in comparison with the naive control (n = 7). B, In the brain, there was regional variation of the distribution of biotin signal (shown by AlexaFluor 488-streptoavidin staining). Coronal section across the thalamus is shown for a naive mouse (top). CSR was associated with an increase of background fluorescence, and somewhat increased diameter of microvessels suggestive of increased capillary filling resulting from hyperemia (bottom). C, In the brainstem, there was also regional variation of biotin distribution in horizontal section across upper medulla at the level of the caudal fourth ventricle. Although the control section shows variation of biotin distribution in different areas, functional hyperemia is most apparent in the medial vestibular nucleus, and dye extravasation is seen in the parapyramidal nucleus in the ventral brainstem (arrows). D, Sodium fluorescein uptake 45 min after intraperitoneal injection in unanaesthetized mice was increased in all brain regions and spinal cord in the CSR mice (n = 7/group) compared with the naive control (n = 8) or those after 24 h of recovery sleep following 6 d of CSR (n = 5); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005. Scale bar, 100 μm.