Figure 1.
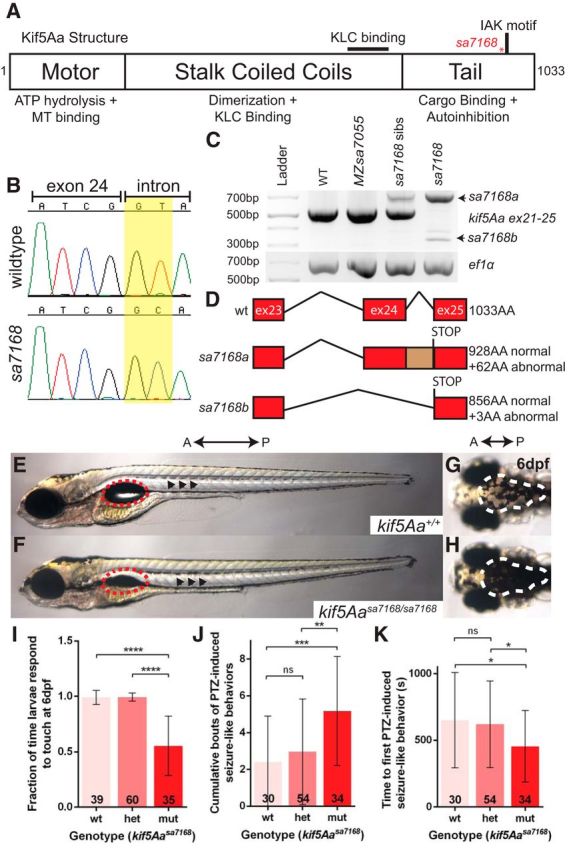
The kif5Aasa7168 mutant allele results in sensorimotor deficits. A, Kif5Aa protein structure. Red asterisk denotes mutation. KLC, Kinesin light chain; MT, microtubule. B, Chromatogram for WT and mutant exon–intron boundaries depicting loss of GT splice donor site in kif5Aasa7168 mutant. C, RT-PCR analysis of kif5Aasa7168 mutant reveals improper splicing of mutant transcripts. D, Novel kif5Aasa7168 mutant transcripts are predicted to lead to premature stop codons and truncated proteins. E, F, Lateral view of 6 dpf larval zebrafish. Red dotted circles denote swim bladder, which is not inflated in kif5Aasa7168 mutants. Black arrowheads denote elevated lateral pigmentation in kif5Aasa7168 mutants. G, H, Dorsal view of 6 dpf larval zebrafish. White dotted line denotes elevated dorsal pigmentation in kif5Aasa7168 mutants. A, Anterior; P, Posterior. I, Touch response of kif5Aasa7168 mutants at 6 dpf. Error bars indicate ±SD; ****p < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA, Tukey's post-test). J, K, Quantification of PTZ seizure-like induction. J, Cumulative bouts of seizures and (K) seizure latency. Error bars indicate ±SD; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA, Tukey's post-test).
