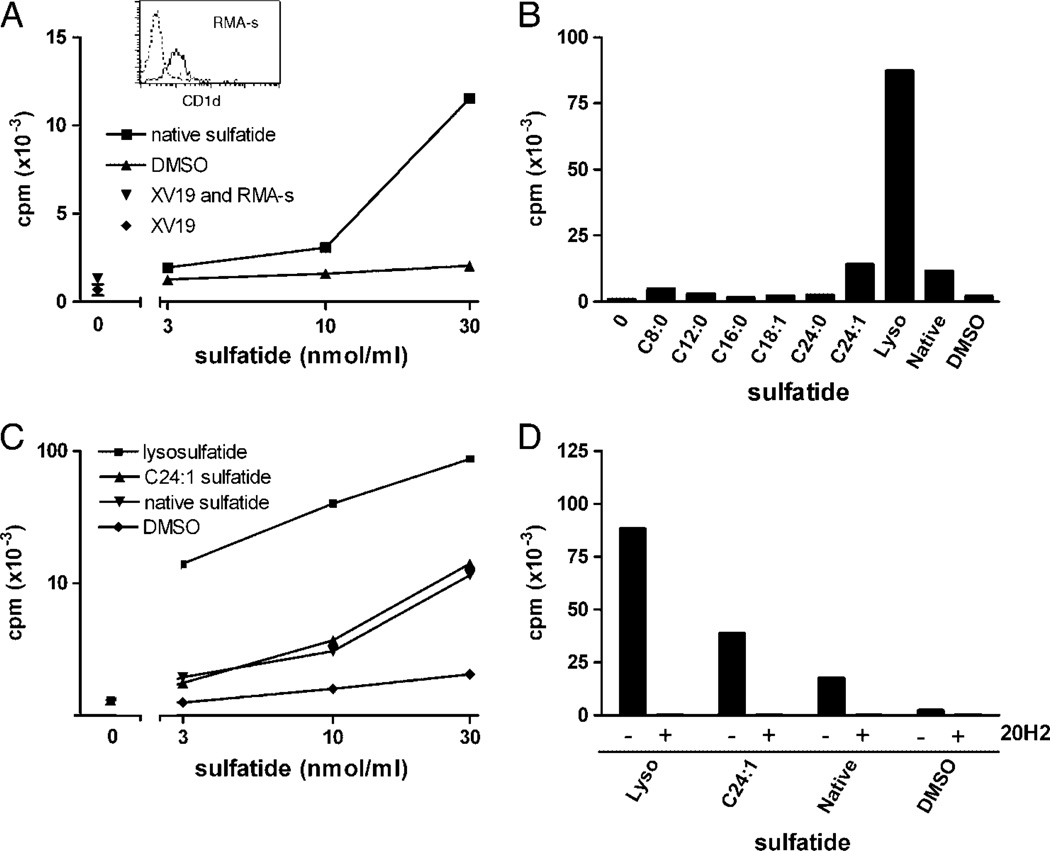
Figure 2.
Activation of the NKT-cell hybridoma XV19 by distinct sulfatide isoforms using RMA-S cells as APC. RMA-S cells (50 × 103 cells/well) were pulsed with the indicated sulfatide isoforms or vehicle (DMSO) before the addition of XV19 NKT hybridoma cells (40 × 103 cells/well). Activation was measured as IL-2 secretion determined in a CTLL-2 bioassay as described in Materials and methods. (A) Different concentrations of native sulfatide (squares) or vehicle (DMSO) were used to stimulate XV19 NKT-cell hybridoma cells. Inset: CD1d expression of RMA-S cells was determined by flow cytometry (dotted line; unstained cells and solid line; CD1d–stained cells). (B) XV19 cells were stimulated with RMA-S cells pre-pulsed with 30 nmol/mL of the indicated sulfatide isoforms (see Fig. 1 and Table 1 for structures of sulfatide isoforms) or vehicle control. (C) XV19 cells were stimulated with a titration of selected sulfatide isoforms presented on RMA-S cells. (D) RMA-S cells were pre-pulsed with lysoe, C24:1 sulfatide or native sulfatide (30 nmol/mL), incubated with or without the CD1d mAb 20H2 [39] for 15 min, followed by addition of the XV19 NKT-cell hybridoma cells. Data shown are from one representative experiment of at least three (A–C) or two (D) (mean of duplicate cultures). Lyso, lysosulfatide.