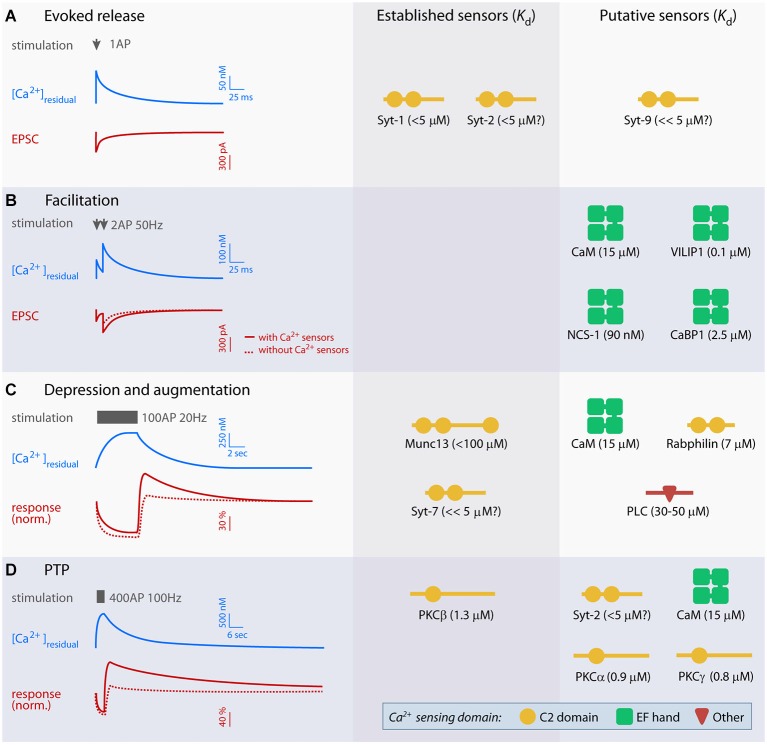
Figure 1.
Overview of established and putative presynaptic Ca2+ sensors in evoked release and short-term plasticity (STP). Left panel displays idealized traces of [Ca2+]residual and excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs; A and B) or baseline-normalized responses (C and D) during synaptic plasticity based on experiments at parallel fiber synapses, mossy fiber-CA3 synapses, the crayfish neuromuscular junction and the calyx of Held. Typical stimulation paradigms used to elicit various forms of STP are indicated in gray. Scale bars are approximate, but note that the amplitude and kinetics of the Ca2+ signal and STP vary significantly between preparations. Right panels show established and putative Ca2+ sensors for evoked release (A) and each form of STP (B–D), and their Ca2+ dissociation constant (Kd). Kd values were obtained from: syt-1 C2AB (with PIP2) (van den Bogaart et al., 2012), free calmodulin (CaM; Xia and Storm, 2005), visin-like protein (VILIP-1) (myristroylated) (Li et al., 2011), neuronal calcium sensor 1 (NCS-1) (myristroylated) and CaBP1 (Aravind et al., 2008), Munc13 C2B (Shin et al., 2010), Rabphilin C2B (Ubach et al., 1999), PLCδ1 (Grobler and Hurley, 1998) PKCα, -β and γ (Torrecillas et al., 2004). The Kd values of syt-2, -7 and -9 have not been measured directly, but indirect measurements suggest that syt-2 is similar to syt-1, whereas syt-7 and 9 may have lower Kd (Sugita et al., 2002).