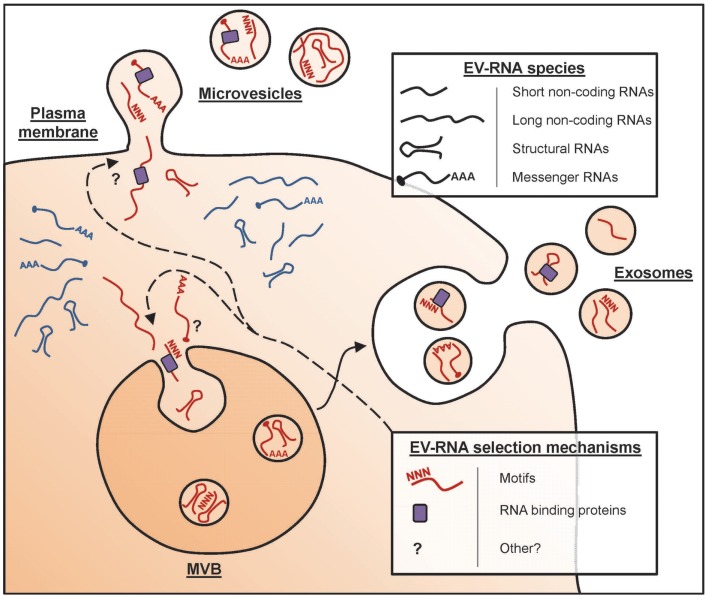
Figure 1.
Formation of RNA-containing EV. In mammalian cells, subpopulations of EV arise in different subcellular compartments. The different types of EV include exosomes, which are released upon fusion of MVB with the plasma membrane, and microvesicles that pinch off directly from the plasma membrane. Depicted are the RNA species detected in EV, i.e., short-non-coding RNAs (e.g., miRNA and tRNA fragments), long-non-coding RNAs, structural RNAs (e.g., Vault RNA and SRP-RNA), and protein-coding mRNAs. It is currently unknown whether all EV contain RNA and whether differences exist in the RNA content of various EV subpopulations. Various studies indicate that selective RNAs are enriched in EV (red), whereas others are preferentially retained in the cell (blue). This RNA sorting process may depend on specific motifs in the RNA sequence and/or may involve the action of RNA-binding proteins (e.g., the ribonucleoprotein A2B1) in addition to yet unidentified mechanisms.