Abstract
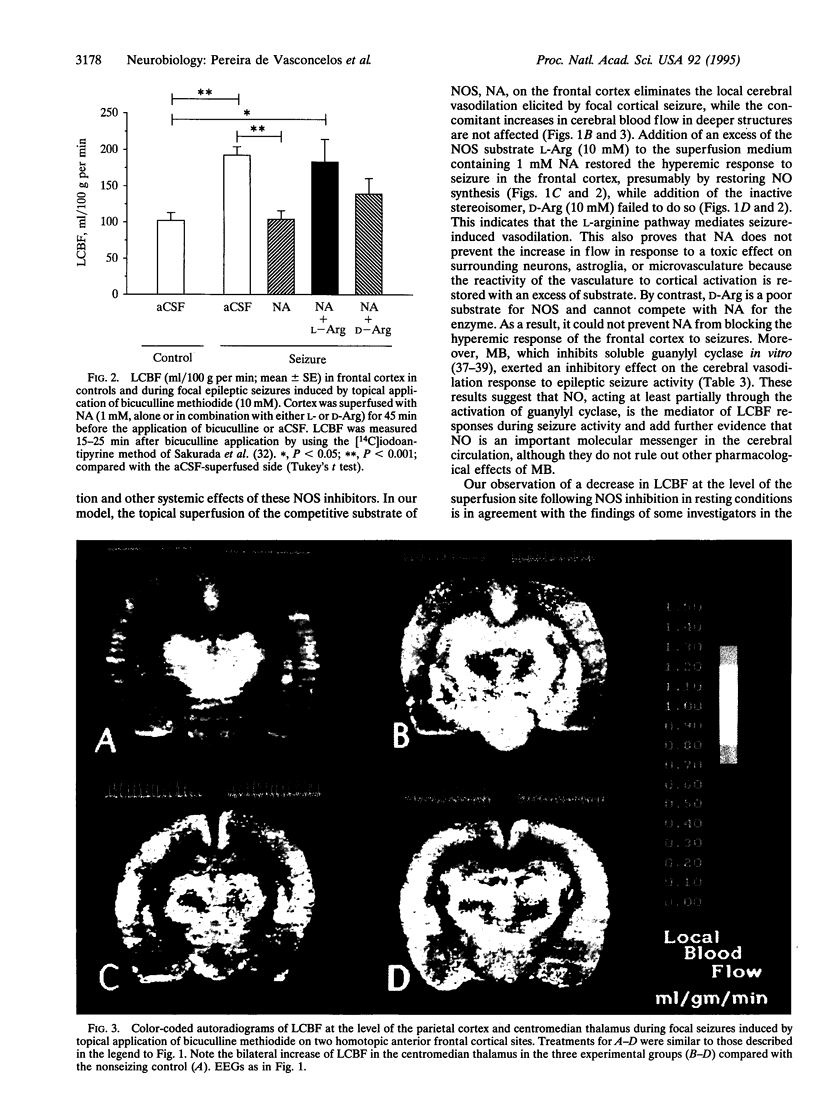
The role of nitric oxide (NO) in the increase in local cerebral blood flow (LCBF) elicited by focal cortical epileptic seizures was investigated in anesthetized adult rats. Seizures were induced by topical bicuculline methiodide applied through two cranial windows drilled over homotopic sites of the frontal cortex, and LCBF was measured by quantitative autoradiography by using 4-iodo[N-methyl-14C]antipyrine. Superfusion of an inhibitor of NO synthase, N omega-nitro-L-arginine (NA; 1 mM), for 45 min abolished the increase of LCBF induced by topical bicuculline methiodide (10 mM) [164 +/- 18 ml/100 g per min in the artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF)-superfused side and 104 +/- 12 ml/100 g per ml in the NA-superfused side; P < 0.005]. This effect was reversed by coapplication of an excess of L-arginine substrate (10 mM) (218 +/- 22 ml/100 g per min in the aCSF-superfused side and 183 +/- 31 ml/100 g per min in the NA + L-Arg-superfused side) but not by 10 mM D-arginine, a stereoisomer with poor affinity for NO synthase (193 +/- 17 ml/100 g per min in the aCSF-superfused side and 139 +/- 21 ml/100 g per min in the NA + D-Arg-superfused side; P < 0.005). Superfusion of the guanylyl cyclase inhibitor methylene blue attenuated the LCBF increase elicited by topical bicuculline methiodide by 25% +/- 16% (P < 0.05). The present findings suggest that NO is the mediator of the vasodilation in response to focal epileptic seizures.
Full text
PDF
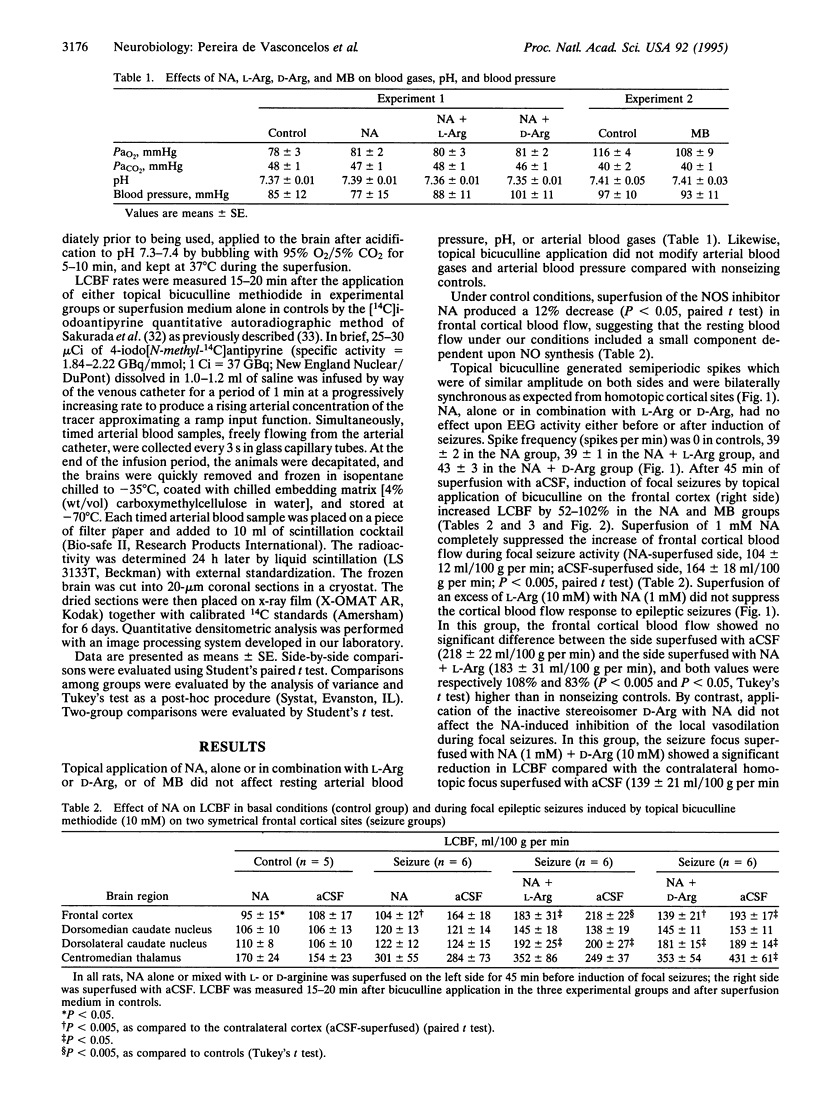
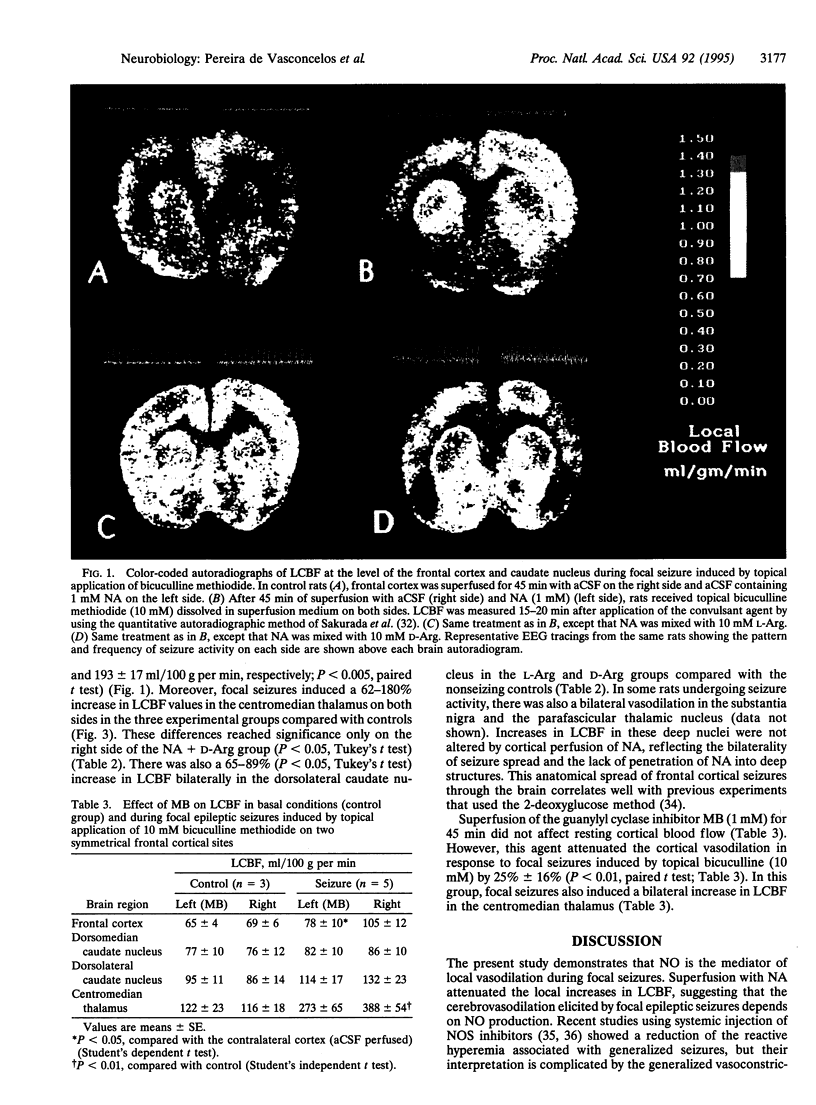

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi T., Inanami O., Sato A. Nitric oxide (NO) is involved in increased cerebral cortical blood flow following stimulation of the nucleus basalis of Meynert in anesthetized rats. Neurosci Lett. 1992 May 25;139(2):201–204. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90552-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akgören N., Fabricius M., Lauritzen M. Importance of nitric oxide for local increases of blood flow in rat cerebellar cortex during electrical stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):5903–5907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):768–770. doi: 10.1038/347768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan J. E., Phillis J. W. The role of nitric oxide in the regulation of cerebral blood flow. Brain Res. 1993 May 7;610(2):248–255. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91408-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins R. C., Kennedy C., Sokoloff L., Plum F. Metabolic anatomy of focal motor seizures. Arch Neurol. 1976 Aug;33(8):536–542. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500080014003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirnagl U., Lindauer U., Villringer A. Role of nitric oxide in the coupling of cerebral blood flow to neuronal activation in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Jan 4;149(1):43–46. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90343-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer M. A., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide synthase: irreversible inhibition by L-NG-nitroarginine in brain in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):1136–1141. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90403-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faraci F. M., Breese K. R. Nitric oxide mediates vasodilatation in response to activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in brain. Circ Res. 1993 Feb;72(2):476–480. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.2.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faraci F. M., Heistad D. D. Does basal production of nitric oxide contribute to regulation of brain-fluid balance? Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 2):H340–H344. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.2.H340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa D. G., Dwyer B. E., Wasterlain C. G. Preferential blood flow to brainstem during generalized seizures in the newborn marmoset monkey. Brain Res. 1986 Nov 5;397(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91369-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gally J. A., Montague P. R., Reeke G. N., Jr, Edelman G. M. The NO hypothesis: possible effects of a short-lived, rapidly diffusible signal in the development and function of the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3547–3551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Charles S. L., Chess-Williams R. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor release on activation of NMDA receptors suggests role as intercellular messenger in the brain. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):385–388. doi: 10.1038/336385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J. Glutamate, nitric oxide and cell-cell signalling in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Feb;14(2):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90022-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iadecola C., Beitz A. J., Renno W., Xu X., Mayer B., Zhang F. Nitric oxide synthase-containing neural processes on large cerebral arteries and cerebral microvessels. Brain Res. 1993 Mar 19;606(1):148–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91583-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iadecola C. Does nitric oxide mediate the increases in cerebral blood flow elicited by hypercapnia? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3913–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iadecola C., Nakai M., Mraovitch S., Ruggiero D. A., Tucker L. W., Reis D. J. Global increase in cerebral metabolism and blood flow produced by focal electrical stimulation of dorsal medullary reticular formation in rat. Brain Res. 1983 Aug 1;272(1):101–114. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Biological actions and properties of endothelium-derived nitric oxide formed and released from artery and vein. Circ Res. 1989 Jul;65(1):1–21. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Biosynthesis and metabolism of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:535–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Heme-dependent activation of guanylate cyclase by nitric oxide: a novel signal transduction mechanism. Blood Vessels. 1991;28(1-3):67–73. doi: 10.1159/000158845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto J., Yoshinaga M., Yang S. P., Krasney E., Krasney J. Methylene blue inhibits hypoxic cerebral vasodilation in awake sheep. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1992 Dec;73(6):2226–2232. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1992.73.6.2226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Palacios M., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Formation of nitric oxide from L-arginine in the central nervous system: a transduction mechanism for stimulation of the soluble guanylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5159–5162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovách A. G., Szabó C., Benyó Z., Csáki C., Greenberg J. H., Reivich M. Effects of NG-nitro-L-arginine and L-arginine on regional cerebral blood flow in the cat. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:183–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koźniewska E., Oseka M., Styś T. Effects of endothelium-derived nitric oxide on cerebral circulation during normoxia and hypoxia in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1992 Mar;12(2):311–317. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1992.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leniger-Follert E. Mechanisms of regulation of cerebral microflow during bicuculline-induced seizures in anaesthetized cats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1984 Jun;4(2):150–165. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1984.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrae I. M., Dawson D. A., Norrie J. D., McCulloch J. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis: effects on cerebral blood flow and glucose utilisation in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1993 Nov;13(6):985–992. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1993.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B. S., Nilsson B. Cerebral blood flow and metabolic rate early and late in prolonged epileptic seizures induced in rats by bicuculline. Brain. 1976 Sep;99(3):523–542. doi: 10.1093/brain/99.3.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers P. R., Minor R. L., Jr, Guerra R., Jr, Bates J. N., Harrison D. G. Vasorelaxant properties of the endothelium-derived relaxing factor more closely resemble S-nitrosocysteine than nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):161–163. doi: 10.1038/345161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehlig A., Pereira de Vasconcelos A., Boyet S. Postnatal changes in local cerebral blood flow measured by the quantitative autoradiographic [14C]iodoantipyrine technique in freely moving rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1989 Oct;9(5):579–588. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1989.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northington F. J., Matherne G. P., Berne R. M. Competitive inhibition of nitric oxide synthase prevents the cortical hyperemia associated with peripheral nerve stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6649–6652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):664–666. doi: 10.1038/333664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce W. J., Reynier-Rebuffel A. M., Lee J., Aubineau P., Ignarro L., Seylaz J. Effects of methylene blue on hypoxic cerebral vasodilatation in the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Aug;254(2):616–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelligrino D. A., Miletich D. J., Albrecht R. F. Diminished muscarinic receptor-mediated cerebral blood flow response in streptozotocin-treated rats. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):E447–E454. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.262.4.E447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Endothelium-dependent and nitrovasodilator-induced relaxation of vascular smooth muscle: role of cyclic GMP. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1983;9(4-5):281–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raszkiewicz J. L., Linville D. G., Kerwin J. F., Jr, Wagenaar F., Arneric S. P. Nitric oxide synthase is critical in mediating basal forebrain regulation of cortical cerebral circulation. J Neurosci Res. 1992 Sep;33(1):129–135. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490330116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud-Monnet A. S., Pinard E., Borredon J., Seylaz J. Blockade of nitric oxide synthesis inhibits hippocampal hyperemia in kainic acid-induced seizures. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1994 Jul;14(4):581–590. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1994.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurada O., Kennedy C., Jehle J., Brown J. D., Carbin G. L., Sokoloff L. Measurement of local cerebral blood flow with iodo [14C] antipyrine. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):H59–H66. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1978.234.1.H59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide: first in a new class of neurotransmitters. Science. 1992 Jul 24;257(5069):494–496. doi: 10.1126/science.1353273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonntag M., Deussen A., Schrader J. Role of nitric oxide in local blood flow control in the anaesthetized dog. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Feb;420(2):194–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00374990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Gotoh F., Gomi S., Takashima S., Mihara B., Shirai T., Nogawa S., Nagata E. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis induces a significant reduction in local cerebral blood flow in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jun 10;127(1):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90911-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q., Kjaer T., Jørgensen M. B., Paulson O. B., Lassen N. A., Diemer N. H., Lou H. C. Nitric oxide does not act as a mediator coupling cerebral blood flow to neural activity following somatosensory stimuli in rats. Neurol Res. 1993 Feb;15(1):33–36. doi: 10.1080/01616412.1993.11740103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q., Paulson O. B., Lassen N. A. Effect of nitric oxide blockade by NG-nitro-L-arginine on cerebral blood flow response to changes in carbon dioxide tension. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1992 Nov;12(6):947–953. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1992.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn H. R., Welsh J. E., Rubio R., Berne R. M. Changes in brain adenosine during bicuculline-induced seizures in rats. Effects of hypoxia and altered systemic blood pressure. Circ Res. 1980 Oct;47(4):568–577. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.4.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]