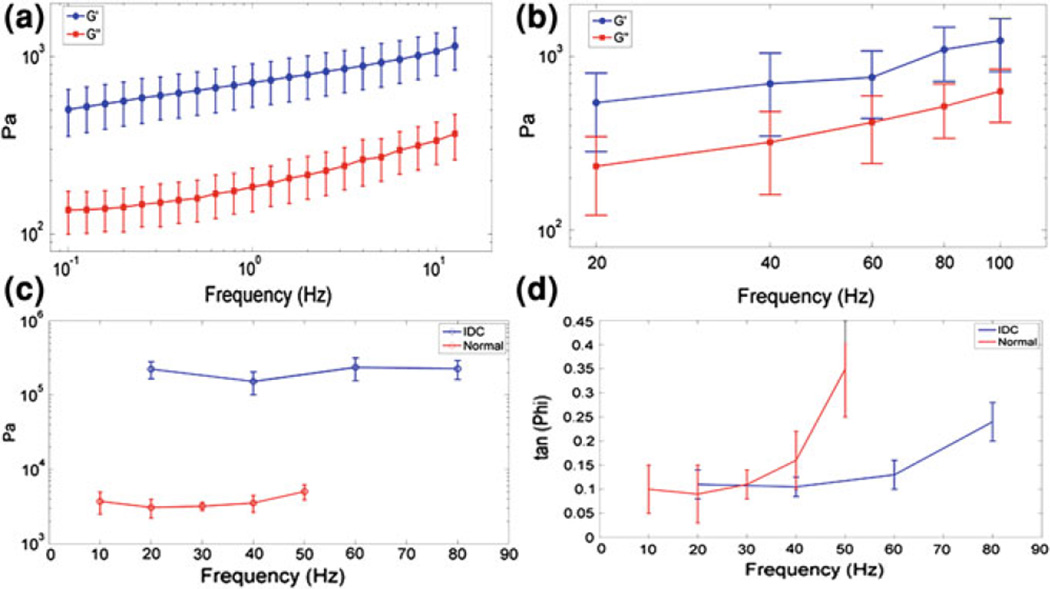
Figure 5.
HMI viscoelasticity estimation: Ex vivo porcine liver specimens (n = 7): Shear storage modulus (G′) (1,070 ± 338 Pa at 10 Hz) and shear loss modulus (G″) (337 ± 90 Pa at 10 Hz) versus frequency for both a rheometry and b HMI; Ex vivo human breast specimens (n = 2): c Shear storage modulus (3.71 ± 0.2 and 223.6 ± 57.1 kPa) 0.40 ± 0.2 kPa (10 Hz) and 24.56 ± 0.7 kPa (20 Hz) and d tan(Φ) (equivalent to shear loss modulus, 0.40 ± 0.2 kPa (10 Hz) and 24.5 ± 6.7 kPa (20 Hz)) versus frequency for both normal breast and IDC, respectively. Errobars denote one standard deviation over five measurements obtained in each specimen