Figure 1.
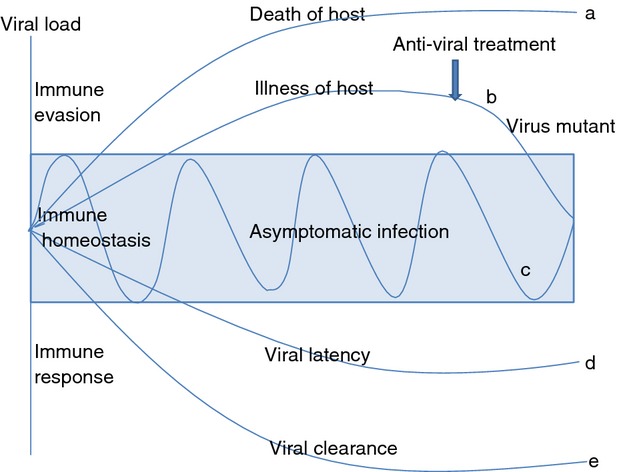
Viral persistence and immune homeostasis. With high viral load infection, virus may evade host immunity, leading to death (a) or illness (b) of the host. With anti-viral treatment, viral load may be reduced, leading to viral clearance or latency. Meanwhile, anti-viral treatment may cause mutation in the virus and drug-resistance (b). When immune homeostasis is maintained, the host exhibits asymptomatic persistent infection, whereby the immune system fight against the virus; and viral load fluctuates during chronic infection (c). Under a strong host immune response, viral infection may become latent (d) or be cleared (e).
