Figure 4.
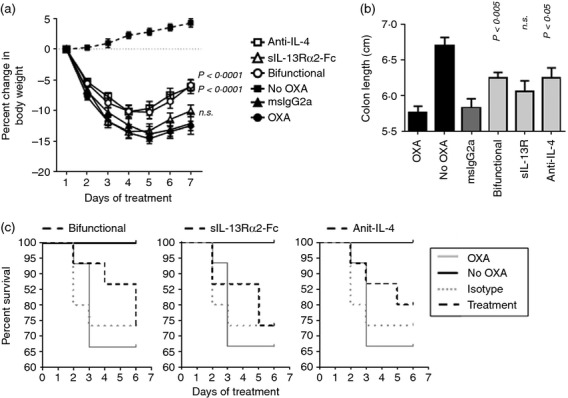
Activity of anti-interleukin-4 (IL-4), sIL-13Rα2-Fc and bifunctional IL-4/IL13 antagonist (3 mg/kg) in oxazolone-induced colitis. Female SJL/J mice were sensitized and challenged with oxazolone as described above. Starting the day before intrarectal challenge (Day −1), mice were given the protein therapeutics at 3 mg/kg intraperitoneally, every 2 days. Control animals were given oxazolone but no treatment (OXA), were given OXA and treated with mouse IgG2a control, or had no disease induction (no OXA). The no OXA group contained six animals. All other groups contained 15 animals on day 0. (a) Body weight throughout the course of treatment. P-values were determined by two-way analysis of variance in comparison with the mouse IgG2a-treated control group. (b) Colon length at time of death. P-values were determined by t-test in comparison to the mouse IgG2a-treated control group. (c) Kaplan–Meier curves, showing % survival throughout the course of treatment. In separate panels, survival of treatment groups is plotted in relation to the OXA, no OXA, and mouse IgG2a control groups; bifunctional antagonist (left), sIL-13Rα2-Fc (middle), anti-IL-4 (right). There were no statistically significant differences in survival between mice in these groups and those given mouse IgG2a control, as determined by Mantel–Cox log rank test.
