Figure 5.
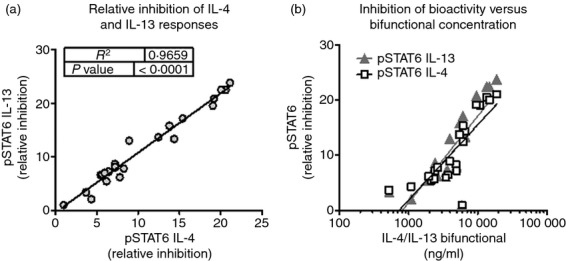
Interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13 neutralization capacity in sera of mice from oxazolone-induced colitis model is proportional to serum concentration of bifunctional antagonist. Female SJL mice were sensitized and challenged with oxazolone as described above. Starting the day before intrarectal challenge (Day −1), mice were administered bifunctional IL-4/IL-13 antagonist at 3 or 8 mg/kg intraperitoneally, every 2 days. On Day 8, sera were collected and titres of antagonist were measured by ELISA. BaF3 cells expressing IL-4 and IL-13 receptors were incubated with sub-optimal concentrations of murine IL-4 or IL-13, in the presence of serum dilutions, for 30 min at 37°. Cells were fixed, permeabilized and stained for expression of phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6). The presence of IL-4 or IL-13 neutralization activity in the sera reduced the STAT6 phosphorylation response to exogenous murine IL-4 or IL-13. (a) The relative IL-4 or IL-13 neutralization activity of individual serum samples was evaluated as the per cent inhibition of the pSTAT6 response, corrected for serum dilution. The relative potency of IL-4 and IL-13 neutralization was proportional. (b) IL-4 or IL-13 neutralization activity, plotted as a function of serum titer of IL-4/IL-13 antagonist.
