Figure 7.
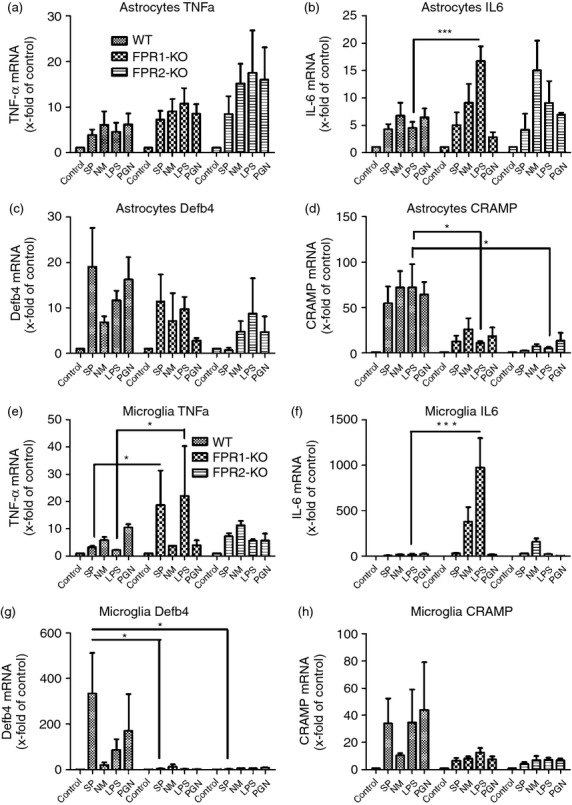
Bacterial supernatants induced pro-inflammatory cytokines and antimicrobial peptides expression in primary glial cells. Astrocytes and microglial cells from formyl peptide receptor 1 knockout (FPR1-KO) or FPR2-KO or wild-type (WT) mice were incubated with bacterial supernatants of Gram-positive bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae (SP) or Gram-negative bacterium Neisseria meningitidis (NM) and bacterial cell wall components lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or peptidoglycan (PGN) for 24 hr. The mRNA expression levels of tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (a, e), interleukin-6 (IL-6) (b, f), β-defensin 4 (c, g) and cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide (CRAMP) (d, h) were determined by real-time RT-PCR. Data were assessed from six independent experiments in duplicate. An asterisk indicates a significant difference between treated WT and treated FPR1-KO or FPR2-KO glial cells as determined by analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni test (*P < 0·05; ***P < 0·001).
