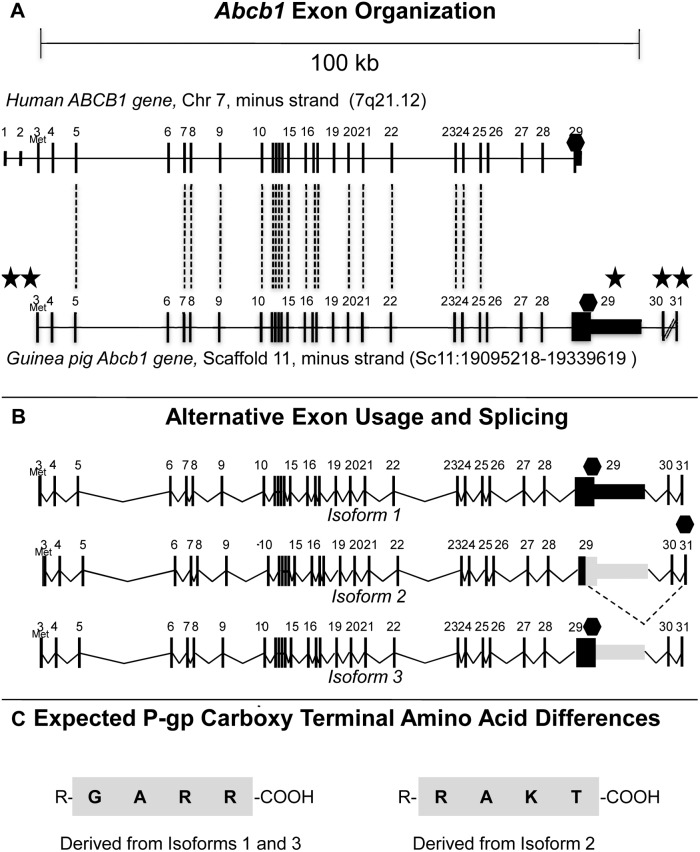
Figure 1. Guinea pig Abcb1 gene, transcripts and C-terminal amino acid differences.
A. Guinea pig Abcb1 locus showing the relative localization of exons (bars) on the coding (minus) strands and in the 5′- to -3′ (left-right) orientation relative to that of the corresponding human ABCB1 locus (above). Dashed lines join highly homologous exons. Diagram drawn to scale. Stars indicate major differences between guinea pig and human P-gp, including the absence of the first two exons, a 2.8 kb exon 29, and the presence of two additional terminal exons, exons 30 and 31. Diagonal lines between exons 30 and 31 represent a longer region than can be represented here. B. Composition of guinea pig ABCB1 transcripts following alternate exon usage and alternative splicing. Note that exons 3 to 28 are common to all three isoforms. Dotted lines represent spliced junctions; Met represents start codon (AUG); Hexagons represent stop codons (UAA). Diagram drawn to scale. C. The 4 carboxy terminal amino acids of the guinea pig P-gp proteins according to in silico translation. R– = the rest of the protein; -COOH = the carboxylic acid tail. Note that diagrams based on results returned from BLAST or BLAT against the UCSC 2008 guinea pig genome assembly change periodically as the assembly evolves; hence, results regarding nucleotide sequences especially intron sizes are subject to change.