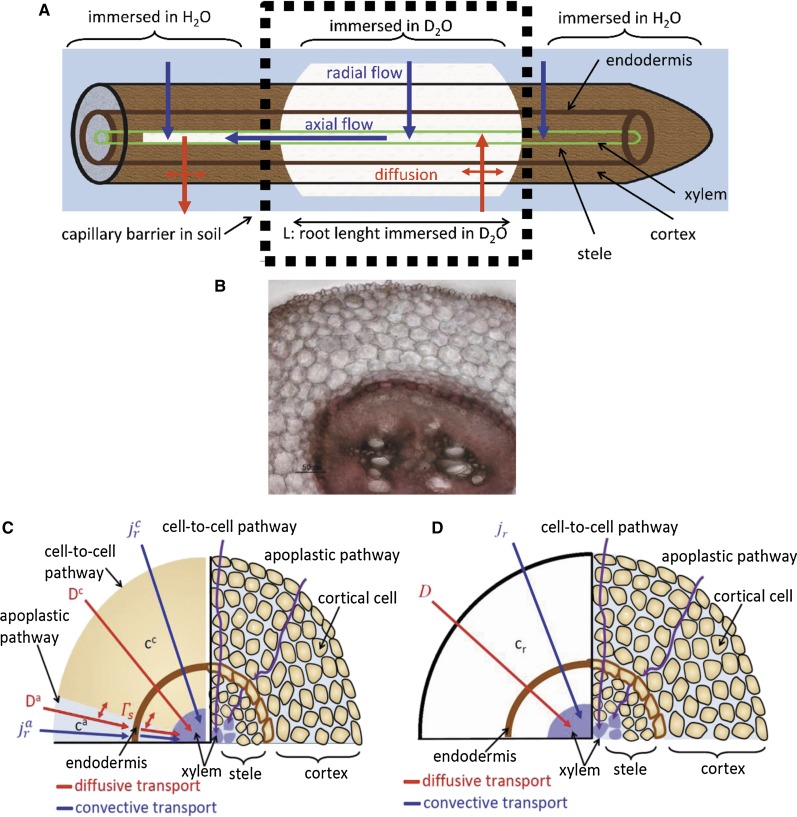
Figure 2.
Illustration of D2O transport into a root partially immersed in D2O. A, Diffusion and convection along a root. Water flows radially to the xylem radius. In the xylem, water flows longitudinally. B, Cross section of a lupine root at a distance of 12 cm from the root tip. C, Representation of the root tissue and its effect on D2O transport in the composite transport model. D, Simplified model in which the different pathways are lumped together in a single averaged pathway across the root tissue. Here, ca and cc are the concentrations of D2O in the apoplastic and symplastic pathways, respectively; cr is the concentration of D2O in the root; Da and Dc are the diffusion coefficients of D2O in the apoplastic and symplastic pathways, respectively; D is the diffusion coefficient of D2O in the root assuming the root as a uniform tissue; 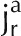 and
and 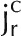 are radial fluxes of water in the apoplastic and symplastic pathways, respectively; jr is the radial flux of water into the root; and Γs is the exchange term of D2O between the apoplastic and cell-to-cell pathways.
are radial fluxes of water in the apoplastic and symplastic pathways, respectively; jr is the radial flux of water into the root; and Γs is the exchange term of D2O between the apoplastic and cell-to-cell pathways.