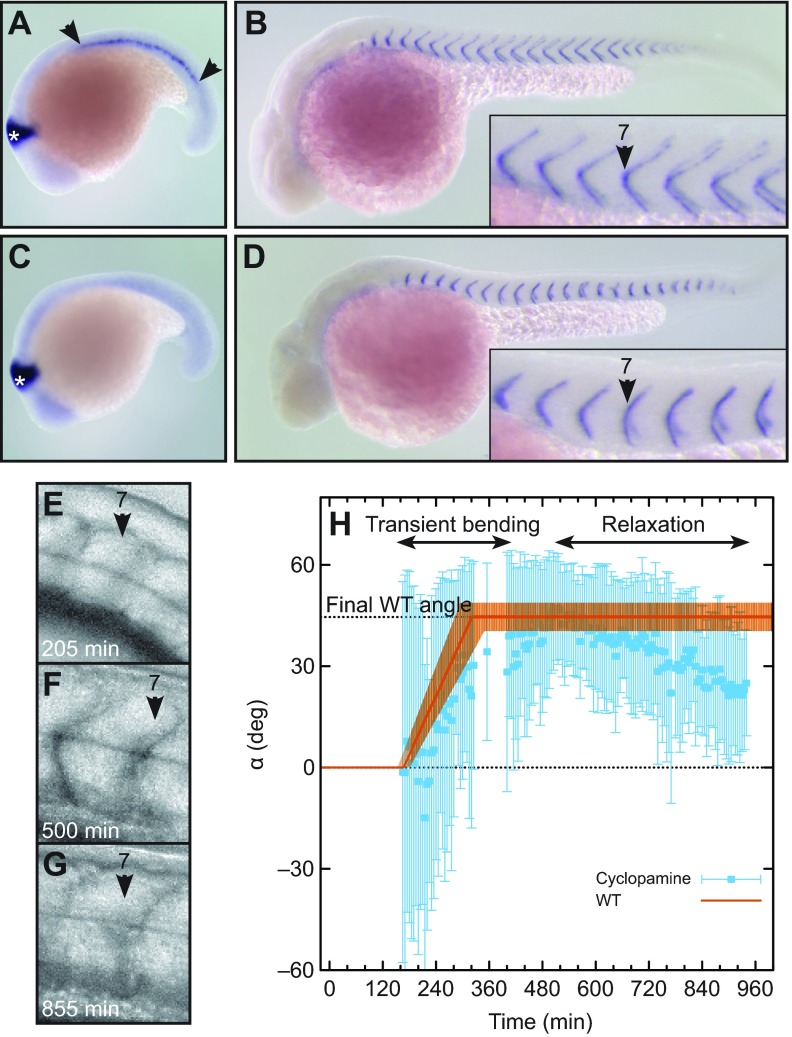
Fig. 4.
Role of muscle pioneers in chevron maintenance, but not formation. (A,B) Embryos treated with 0.2% DMSO alone (control). (A) engrailed2 (en2) in situ hybridization at 18 somite stage. Muscle pioneers are stained by en2 (area between arrowheads). The midbrain is marked with a white asterisk. (B) cb1045 in situ hybridization at 36 hpf (hours post-fertilization) to visualize segment boundaries. (C,D) Embryos treated with 7.5 μmol l−1 cyclopamine from bud stage. (C) en2 in situ hybridization at 18 somite stage. Muscle pioneers are absent. (D) cb1045 in situ hybridization at 36 hpf. Boundaries are U-shaped. (E–G) Lateral views of segment 7 of an embryo treated with 7.5 μmol l−1 cyclopamine from bud stage. (E) Newly formed segment is cuboidal. (F) At 500 min, the segment has a clear chevron shape. (G) At 855 min, the chevron relaxed into a U-shape. (H) Quantification of chevron angles of the segment shown in E–G (blue squares and error bars). The orange line shows the typical bending of an immobile embryo (piecewise linear function with parameters for segment 7 from Fig. 3, uncertainty depicted by the transparent orange area). WT, wild-type.