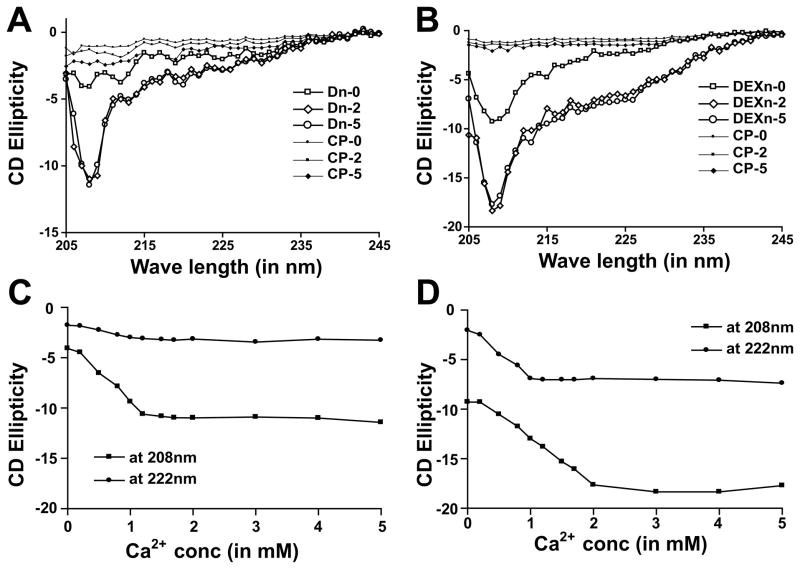
Figure 2. Dn and DEXn motifs undergo distinct structural changes upon exposure to Ca2+.
(A) Dn-motif peptide acquires coiling when Ca2+-concentration is increased. At 0 mM Ca2+ (Dn-0), the Dn-motif remains in almost linear conformation. In 2 mM and 5 mM Ca2+ (Dn-2 and Dn-5 respectively) Dn-peptide shows marked increase in the negative ellepticity at 208 nm. (B) DEXn-motif peptide acquires helical content in addition to coiling upon Ca2+-binding. At 0 mM Ca2+ (DEXn-0), the DEXn-peptide remains in coiled conformation. In 2 mM and 5 mM Ca2+ (DEXn-2 and DEXn-5 respectively) DEXn-peptide shows marked increase in the negative ellepticity both at 222 and 208nm. Plot of CD ellepticity at 208 and 222nm for Dn-peptide (C) and DEXn-peptide (D) with increasing Ca2+-concentration. For the DEXn-peptide, the transition of helical content is achieved ~1 mM Ca2+, while that of coiling is achieved ~2 mM Ca2+. The Dn-peptide achieves the transition of coiling content ~1 mM Ca2+. Control peptide is denoted as CP.