Figure 2.
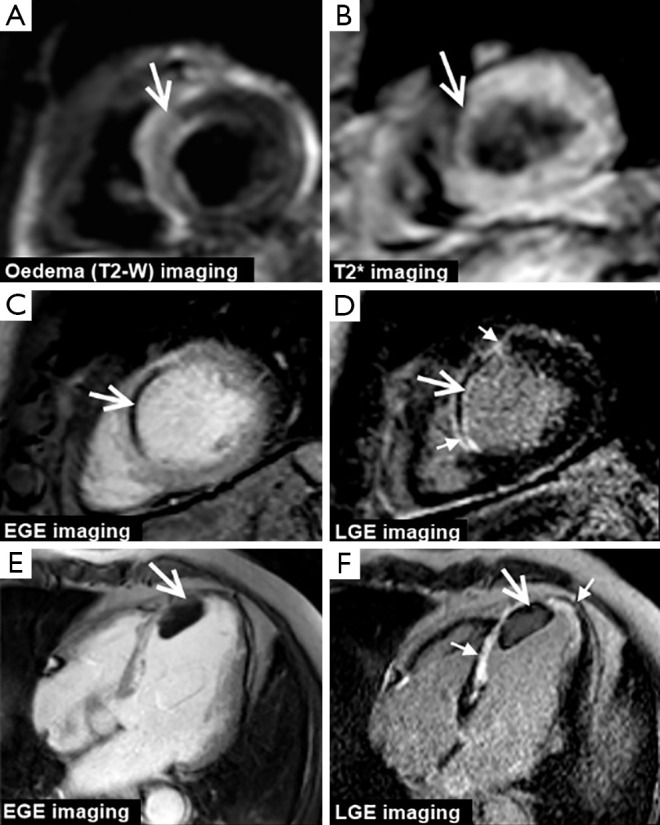
CMR in acute MI. The top row shows mid-ventricular short-axis images from a patient on day 3 following an acute septal STEMI. Myocardial edema i.e., the ‘area-at risk’ is seen as high-signal intensity on T2 weighted imaging (arrow, A) and a central core of reperfusion hemorrhage is seen as low signal intensity on T2* imaging (arrow, B). The middle row shows mid-ventricular short-axis images images from another patient with an occlusion of the proximal left anterior descending artery. Both EGE and LGE imaging show a core of non-contrast uptake i.e., microvascular obstruction (large arrows, C and D) within a transmural septal wall MI which is outlined by hyperenhancement on LGE imaging (small arrows, D). The bottom row shows 4-chamber images from a 55-year-old man with a recent LAD territory MI. EGE and LGE imaging show a non-enhancing (and therefore avascular) mass typical of LV thmrobus. LGE imaging demonstrates that the thrombus overlies mid to apical antero-septum infarction seen as hyperenhancement (small arrows, F). CMR, cardiovascular magnetic resonance; MI, myocardial infarction; EGE, early gadolinium enhancement; LGE, late gadolinium enhancement; LV, left ventricular.
