Fig. 2.
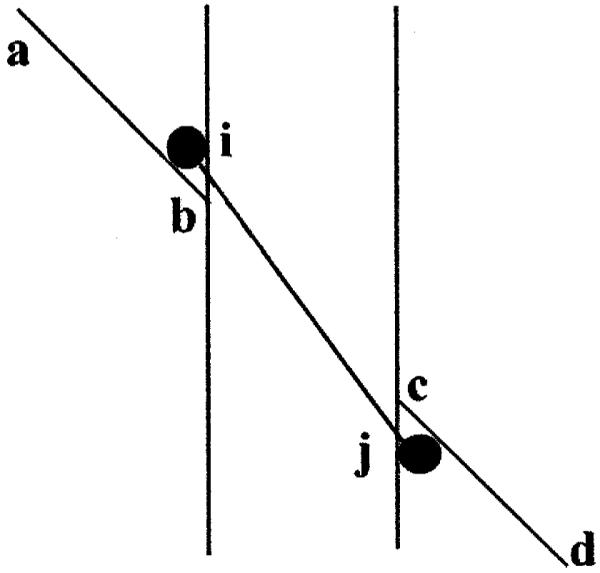
The figure illustrates a model for the Poggendorff illusion. The observer judges lines a, b and c, d to be collinear when they have the same orientation and this orientation is the same as the virtual line joining their points of intersection b, c with the vertical parallels, e, f and g, h. However, these termination points are mislocated following spatial filtering at points i, j. The orientation of the virtual line i, j thus differs from that of a, b, c, d and an illusory misalignment results. For details of the filtering process see the text.
