Figure 1.
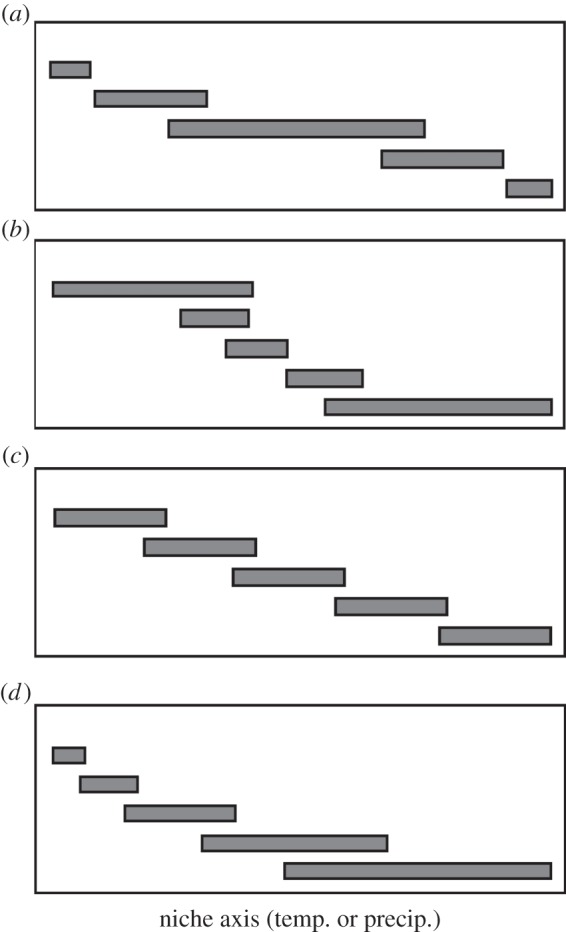
Hypothetical examples illustrating different possible relationships between climatic niche breadth and niche position (adapted from [13], their fig. 1). Each grey bar represents the range of values where a species occurs on a climatic niche axis (temperature, precipitation). In (a), species that occur in the most extreme positions on the niche axis have narrower niche widths (i.e. they are more specialized for these extreme conditions). In (b), species that occur in more extreme conditions occur under a broader range of conditions than other species in the clade, and therefore have wider niche widths. In (c), species have similar niche widths regardless of position on this niche axis. In (d), species that occur on one end of the gradient are more specialized, whereas species that occur on the other end are more generalized (i.e. have broader niche widths).
