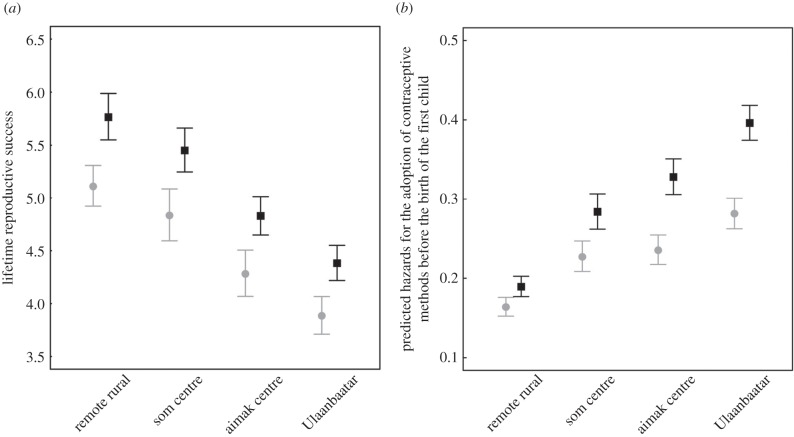
Figure 1.
Household wealth and reproductive outcomes along a rural–urban gradient. (a) Predicted means (and s.e.) for LRS among post-reproductive women (older than 45 years; n = 815). LRS is 12% higher among the wealthiest in all regions. (b) Predicted hazards (and s.e.) for the adoption of contraceptive methods before the birth of the first child (n = 9314). Wealthy women are more likely to adopt contraceptive methods (either modern or traditional) before the birth of their first, second and third child, and particularly so in urban areas. Values are reported for married women, atheists and born after 1967. Squares represent women living in rich households and circles represent women living in poor households.