Figure 2.
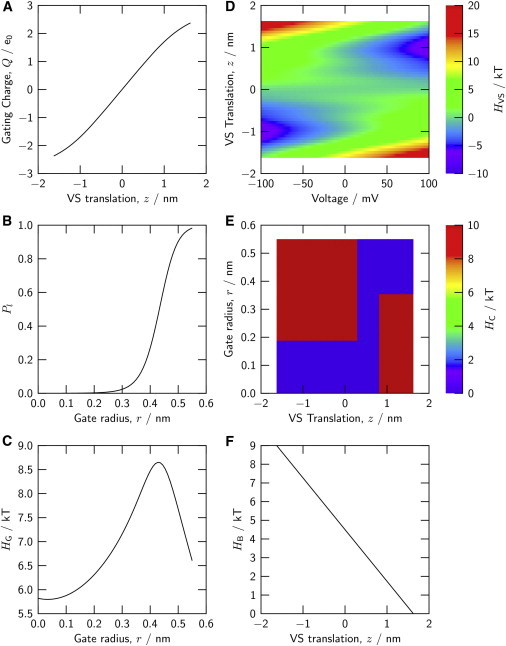
Six relations specify the domains and domain interactions of the channel model. (A) Displaced gating charge Q of a voltage sensor domain as a function of the translational S4 position, z. (B) Probability P1 of the liquid-filled (conducting) configuration of the gate, as a function of the intracellular gate radius, r. (C) Hamiltonian component (gate work) associated with the gate radius r. (D) Hamiltonian component associated with the translational position z of an individual VS domain, as a function of the transmembrane voltage (Eq. 3). (E) Hamiltonian component describing the coupling between a VS domain at translational position z and the hydrophobic gate of radius r. (F) Hamiltonian component describing the energetic bias acting on a VS domain, as function of translational position, z. Panels A and D are predictions by the VS model described in Peyser and Nonner (21); panels B and C are predictions by the gate model in Roth et al. (20). To see this figure in color, go online.
