Abstract
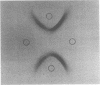
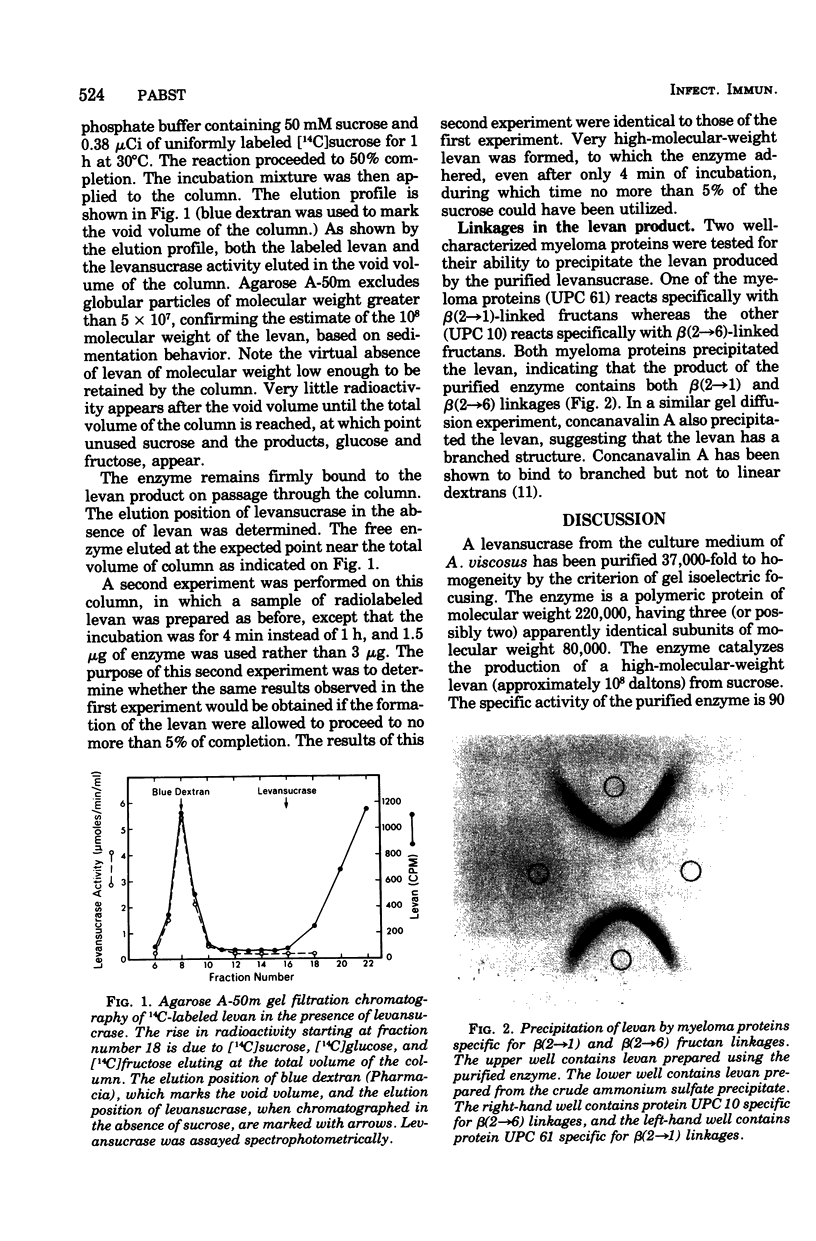
A levansucrase was demonstrated in the growth medium and in association with the cell surface of Actinomyces viscosus. The amount of enzyme produced relative to cell density is not significantly affected by the growth conditions. Sugar alcohols inhibit growth of the cells. The levansucrase hydrolyzes sucrose to produce free glucose and levan; some free fructose is also formed. There is no requirement for cofactors. The Km for sucrose is 12 mM. A variety of heavy metal ions and two disaccharides, lactose and cellobiose, inhibit the enzyme. The levansucrase was purified to homogeneity and has a specific activity of 90 micronmol of glucose release per min per mg. The enzyme has a molecular weight of 220,000 and is composed of subunits of molecular weight 80,000. The levan product contains both beta(2 leads to 1) and beta(2 leads to 6) linkages. The enzyme remains tightly bound to the levan product, resulting in the formation of high-molecular-weight polymer on the order of 10(8) daltons. The possible role of the levan and levansucrase of A. viscosus in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourgeau G., McBride B. C. Dextran-mediated interbacterial aggregation between dextran-synthesizing streptococci and Actinomyces viscosus. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1228–1234. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1228-1234.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. A levansucrase from Streptococcus mutans. Caries Res. 1970;4(2):97–113. doi: 10.1159/000259632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J., Kabat E. A., Liao J., Potter M. Immunochemical studies on mouse myeloma proteins reactive with dextrans or with fructosans and on human antilevans. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):159–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DaCosta T., Gibbons R. J. Hydrolysis of levan by human plaque streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Jun;13(6):609–617. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich J., Stivala S. S., Bahary W. S., Garg S. K., Long L. W., Newbrun E. Levans: I. Fractionation, solution viscosity, and chemical analysis of levan produced by Streptococcus salivarius. J Dent Res. 1975 Mar-Apr;54(2):290–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank R. M., Guillo B., Llory H. Caries dentaires chez le rat gnotobiote inoculé avec Actinomyces viscosus et Actinomyces naeslundii. Arch Oral Biol. 1972 Sep;17(9):1249–1253. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(72)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garszczynski S. M., Edwards J. R. Synthesis of a broth levan by a cell-bound levansucrase from Streptococcus salivarius (SS2). Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Feb;18(2):239–251. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90144-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germaine G. R., Schachtele C. F., Chludzinski A. M. Rapid filter paper assay for the dextransucrase activity from Streptococcus mutans. J Dent Res. 1974 Nov-Dec;53(6):1355–1360. doi: 10.1177/00220345740530061101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., Poretz R. D., So L. L., Yang Y. Protein--carbohydrate interaction. XVI. The interaction of concanavalin A with dextrans from L. mesenteroides B-512-F, L. mesenteroides 9birmingham), Streptococcus bovis, and a synthetic alpha-(1--6)-D-glucan. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Sep 20;127(1):787–794. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90290-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond B. F., Steel C. F., Peindl K. S. Antigens and surface components associated with virulence of Actinomyces viscosus. J Dent Res. 1976 Jan;55:A19–A25. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500111011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell A., Jr, Jordan H. V. Production of an extracellular levan by Odontomyces viscosus. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Apr;12(4):571–573. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Lehner T. Stimulation of human lymphocytes by B-cell mitogens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):347–356. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan H. V., Keyes P. H., Bellack S. Periodontal lesions in hamsters and gnotobiotic rats infected with actinomyces of human origin. J Periodontal Res. 1972;7(1):21–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1972.tb00627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan H. V., Keyes P. H., Lim S. Plaque formation and implantation of Odontomyces viscosus in hamsters fed different carbohydrates. J Dent Res. 1969 Sep-Oct;48(5):824–831. doi: 10.1177/00220345690480053601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llory H., Guillo B., Frank R. M. A cariogenic Actinomyces viscosus--a bacteriological and gnotobiotic study. Helv Odontol Acta. 1971 Oct;15(2):134–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manly R. S., Richardson D. T. Metabolism of levan by oral samples. J Dent Res. 1968 Nov-Dec;47(6):1080–1086. doi: 10.1177/00220345680470061301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Bourgeau G. Dextran-induced aggregation of Actinomyces viscosus. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Dec;20(12):837–841. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90063-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. H., Warner T. N., Palenik C. J., Somers P. J. Levan formation by whole cells of Actinomyces viscosus ATCC 15987. J Dent Res. 1975 Jul-Aug;54(4):906–906. doi: 10.1177/00220345750540043701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Scheinin A., Mäkinen K. K. Effect on plaque of a xylitol-containing chewing-gum. A clinical and biochemical study. Acta Odontol Scand. 1975;33(1):33–40. doi: 10.3109/00016357509004624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Righetti P. G., Drysdale J. W. Isoelectric focusing in gels. J Chromatogr. 1974 Sep 25;98(2):271–321. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)92076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robrish S. A., Reid W., Krichevsky M. I. Distribution of enzymes forming polysaccharide from sucrose and the composition of extracellular polysaccharide synthesized by Streptococcus mutans. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Aug;24(2):184–190. doi: 10.1128/am.24.2.184-190.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B., Hammond B. F. Extracellular polysaccharides of Actinomyces viscosus. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):304–308. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.304-308.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S., Hubersak C., Propas D. Induction of periodontal destruction in gnotobiotic rats by a human oral strain of Actinomyces naeslundii. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Oct;15(10):993–995. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Houte J., Jansen H. M. Levan degradation by streptococci isolated from human dental plaque. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Jul;13(7):827–830. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Hoeven J. S., Vogels G. D., Bekkers M. F. A levansucrase from Actinomyces viscosus. Caries Res. 1976;10(1):33–48. doi: 10.1159/000260187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]